Concrete Floor Insulation
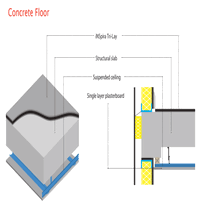
Concrete floor insulation involves selecting suitable materials such as polystyrene foam boards, PIR, XPS, or mineral wool, which are installed on prepared, level subfloors with moisture barriers to prevent dampness. Proper installation techniques include securely fixing the insulation with adhesives or mechanical fastenings and planning for accessibility and space considerations, particularly in areas with limited ceiling heights. Effective insulation enhances energy efficiency, reduces heat loss, guards against moisture ingress, and improves overall comfort within buildings. Ensuring adherence to best practices and regulatory standards is essential for achieving optimal insulation performance and durability.
Types of Materials for Concrete Floor Insulation
Concrete floor insulation employs a variety of materials specifically designed to enhance thermal efficiency, structural integrity, and durability of the finished surface. Polystyrene foam boards, including expanded (EPS) and extruded (XPS), are common choices offering good thermal resistance; however, XPS may experience thermal drift over time, reducing its effectiveness. Uninsulated basements can lose nearly one-third of home heat, making insulation critical for energy savings and comfort. Foam boards such as PIR, XPS, and phenolic provide high compressive strength, making them suitable for load-bearing applications. Ultralight™ thin insulation boards, often less than a quarter of an inch thick, facilitate heat spreading and acoustic separation, particularly in renovation scenarios. Additionally, fibre-based materials like fibre glass and mineral wool are utilised in specific situations where [moisture control is essential. However, these materials tend to have lower compressive strength and often require protective barriers to prevent moisture ingress. The selection of each material depends on specific performance requirements, structural considerations, and available budget, ensuring the most appropriate solution is applied for each project.
Methods for Installing Insulation Under Concrete Floors
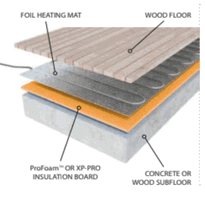
Proper installation of insulation beneath concrete floors begins with careful preparation of the subfloor surface and selecting the appropriate method based on the project’s requirements. Ensuring the floor is level and clean creates a stable base, while installing a vapour barrier prevents moisture from compromising the insulation. Concrete’s porous nature allows ground moisture to permeate, making moisture control essential. The insulation method varies, with options such as rigid foam boards installed directly on the subfloor, or utilising wooden sleepers to support additional layers. The choice depends on factors like headroom, moisture control, and insulation efficiency. Proper planning to accommodate Delivery Conditions & Responsibilities can ensure smooth installation, especially when coordinating delivery times and access. Key steps include: 1. Ensuring a level, clean subfloor to promote stability and effective insulation contact. 2. Installing a vapour barrier to prevent rising damp from affecting the insulation. 3. Securing insulation with appropriate adhesives or mechanical fasteners, such as masonry nails. 4. Maintaining even insulation placement to optimise thermal performance before finishing the floor.
Advantages of Proper Floor Insulation in Concrete Structures
Adequate insulation enhances energy efficiency by reducing heat loss through the floor, which lowers utility bills and diminishes carbon emissions significantly. It also optimises the performance of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems by lessening the demand on these units, thereby extending their lifespan and reducing maintenance costs.
Furthermore, proper insulation serves as a moisture barrier, preventing ground moisture from infiltrating the structure, which helps to avoid dampness and mould growth. This protection not only maintains the structural integrity of the floor but also promotes healthier indoor air quality. [Fibreglass pipe insulation can be used outdoors with protective cladding, contributing to effective moisture control and durability.
In addition, insulation increases thermal comfort by keeping floors warmer, particularly in ground-floor spaces, which can greatly improve occupant comfort. It also reduces noise transmission between levels, creating a more peaceful indoor environment.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Installing insulation in concrete floors presents several physical and technical challenges that can impact its effectiveness and durability. These include limited ceiling height, which may restrict the thickness of insulation such as radiant foam. Uneven or contaminated concrete surfaces must be thoroughly cleaned and repaired to ensure proper adhesion. Ensuring the insulation material has suitable [thermal performance is essential for maximizing energy efficiency. Additionally, moisture within the concrete can cause water absorption, making the use of vapour barriers essential. Tight space constraints require careful selection of materials and precise installation techniques.
Regulatory Standards and Best Practices for Insulating Concrete Floors
Regulatory standards for insulating concrete floors in the UK are established through a combination of national building regulations and industry-specific codes that set out minimum requirements to guarantee energy efficiency, safety, and durability.
The UK Building Regulations Part L (Conservation of Fuel and Power) provides essential guidelines for insulating ground floors, including requirements for perimeter insulation and the inclusion of full under-slab insulation in heated slabs, with updates reflecting advancements in energy performance standards.
Standards aligned with these regulations specify the necessary thermal transmittance, often expressed as U-values, to minimise heat loss through concrete floors. For example, typical requirements call for U-values of no more than 0.18 W/m²K for ground floors in new dwellings, with more stringent targets for energy-efficient or low-carbon buildings.
These standards encourage the use of suitable insulation materials, such as polystyrene (XPS or PIR), and specify minimum insulation thicknesses usually between 100 and 150 millimetres to achieve compliance. Additionally, the use of advanced insulation techniques can significantly improve thermal performance and ensure compliance with evolving standards.
In addition, industry schemes and voluntary labels, such as the UK Green Building Council standards, promote best practices by recommending insulation methods that optimise energy performance while maintaining cost-effectiveness and ease of installation.
These evolving standards directly influence construction practices by setting clear targets for thermal performance, thereby supporting long-term energy savings, occupant comfort, and legal compliance.
Adhering to these principles ensures that concrete floor insulation contributes positively to building energy efficiency, reduces carbon emissions, and aligns with the UK's commitment to sustainable development. Implementation of these standards plays a crucial role in reducing heat loss and improving overall building sustainability.
Conclusion
Implementing appropriate insulation methods and materials for concrete floors enhances thermal performance, reduces energy costs, and helps prevent moisture issues. Following recognised standards and best practices ensures safety, durability, and compliance with UK regulations. Addressing common installation challenges through systematic planning and meticulous execution results in effective, long-lasting insulation solutions. A precise, well-informed approach to insulation selection and installation is vital for optimal structural efficiency and environmental control within concrete-based constructions.