Electric Heat Tracing for Pipes
Electric heat tracing systems utilize resistive heating elements embedded along pipes to provide controlled, efficient heat that prevents freezing and maintains process fluidity. These systems consist of various cable types, including mineral insulated, self-regulating, and flexible resistance cables, each suitable for different applications.
Proper installation involves securing the cables at regular intervals, beginning at the pipe’s end, and ensuring safety measures such as insulation and reliable electrical connections. Attention to correct installation practices helps optimize system performance, safety, and longevity.
Continuing will reveal detailed guidelines to ensure safe, durable, and environmentally friendly pipe heating solutions tailored to the requirements of UK applications.
Overview of Electric Heat Tracing Technology and Its Benefits
Electric heat tracing technology operates by embedding resistive heating elements along the length of pipes, which generate heat when an electrical current passes through them. These elements are in direct contact with the pipe surface, ensuring efficient heat transfer to maintain or raise the temperature of the contents. Modern systems incorporate smart controls and IoT features, providing real-time monitoring and remote operation capabilities. Pipes are typically insulated to reduce heat loss and improve system efficiency, allowing the system to compensate for environmental heat loss and sustain a consistent temperature. The primary benefit of electric heat tracing is its capacity to prevent the freezing of fluids inside pipes, thereby avoiding pipe bursts and process disruptions. It also helps to maintain stable fluid viscosity, ensuring smooth flow throughout the system.
Types of Heat Trace Cables and System Components
There are several primary types of heat trace cables, each designed with specific features to suit different industrial and commercial applications. Understanding these variations helps ensure proper selection and system efficiency.
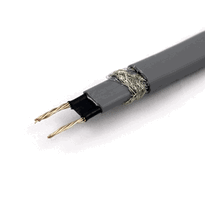
Flexible resistance heating cables feature multiple conductor configurations with corrosion-resistant nickel-plated copper conductors. They're rated for temperatures up to 260°C and are protected by metallic braids to provide mechanical strength and durability.
Mineral insulated (MI) cables are capable of withstanding extreme environments. They can endure temperatures up to 593°C when de-energized, employing magnesium oxide insulation within seamless metal sheaths, ensuring high reliability in harsh conditions.
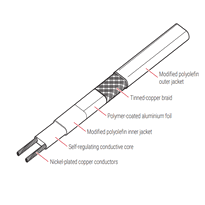
Self-regulating cables adapt their heat output based on ambient temperature conditions. This regulation optimizes energy use and enhances safety, with operational ratings around 150°C.
System components include cold leads and end terminations, which serve the purpose of connecting power safely to the cables and preventing moisture ingress that could compromise system performance.
Protective outer layers and braids provide essential protection against mechanical damage. They also facilitate grounding and shield the cables from electromagnetic interference, ensuring long-term durability and operational safety.
Key Considerations for Safe and Efficient Installation
Key Considerations for Safe and Efficient Installation of Heat Trace Cables
To ensure safe and effective installation of heat trace cables, it's essential to adhere to recommended practices regarding placement, securement, and configuration. Proper placement begins at the end of the circuit, with cables attached at the 4 or 8 o'clock position on the lower half of the pipe. This positioning promotes uniform heat transfer and ease of access during maintenance or inspections.
Secure the cables at intervals not exceeding 30 centimeters using appropriate attachment tape. This ensures that the cables remain in close contact with the pipe, preventing movement that could lead to uneven heating or damage. Applying foil tape beneath the cable on plastic pipes can further optimize heat flow and improve overall system efficiency.
Prior to commencing installation, conduct electrical integrity testing to verify cable functionality and compatibility. Confirm that the pipe and surrounding materials are suitably prepared to withstand any applied pressure and environmental conditions.
Proper planning should also account for suitable insulation, environmental protection, and mechanical safeguards. Incorporating spacers where necessary, avoiding sharp edges, and selecting materials resistant to ultraviolet radiation and moisture will significantly extend the lifespan of the heating system.
Using environmentally sustainable construction materials such as hemp-based insulation can support eco-friendly building practices, reduce embodied carbon, and enhance the durability of installation projects. Following these best practices ensures not only the safety of the installation process but also the reliable and efficient operation of the heat trace system over time.
Conclusion
Proper selection and installation of electric heat tracing systems are essential for maintaining pipe integrity and preventing freezing. Understanding the various types of heat trace cables, system components, and safety considerations ensures effective operation, reduces energy consumption, and minimizes hazards. Following detailed guidelines and best practices during installation guarantees system efficiency and longevity. Ultimately, a well-designed and correctly implemented heat tracing solution supports reliable infrastructure performance, safety compliance, and operational cost savings over its service lifespan.