Electric Pipe Wrap
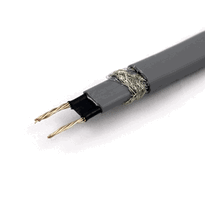
Electric pipe wraps are heating tapes designed to prevent pipe freezing and damage by providing controlled heat to vulnerable pipes in unheated or exposed areas, such as basements or outdoor locations. These wraps are available in various types, including self-regulating and constant-wattage models, with materials like silicone or fiberglass to ensure both safety and durability.
Proper installation is essential for effective protection. This involves securing the tape firmly with thermal-resistant ties, avoiding overlaps that could cause overheating, and carefully following the manufacturer’s instructions. The wraps should be connected to GFCI outlet circuits to minimize electrical risks and ensure safety.
Understanding these key points can help you protect your pipeline more effectively against the cold weather, maintaining the integrity and functionality of your plumbing system throughout the winter months.
Understanding the Function and Benefits of Electric Pipe Wrap
Electric pipe wrap is an effective solution for preventing freezing and damage to pipes during cold weather conditions by delivering direct heat to maintain a consistent internal pipe temperature above freezing point. This method ensures that water inside the pipes doesn't freeze, reducing the risk of expansion and subsequent pipe bursts. It's particularly suitable for exposed, vulnerable pipes located in unheated spaces such as basements, crawl spaces, and outdoor areas. Using these wraps helps to avoid costly repairs, water damage, and potential system failures. When combined with pipe insulation, they enhance freeze protection and, helping to minimise energy consumption and lower utility bills. Proper installation of electric pipe wraps prolongs the lifespan of pipes by preventing corrosion, moisture accumulation, and environmental damage. They are suitable for use on both exterior and interior pipes in vulnerable locations, making them versatile for various scenarios. Overall, they contribute to safer, more reliable plumbing systems in UK buildings, especially during periods of extreme cold.
Types and Materials Used in Heat Tape Technology
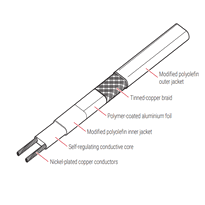
Various types of heat tape technologies are available to meet different pipe protection needs, each employing unique mechanisms to generate and regulate heat. Self-regulating heat tapes adjust their output based on ambient temperature, increasing heat in colder spots and reducing it near warmer areas. This responsive feature helps prevent overheating and conserves energy, making them suitable for a range of applications. Self-regulating tapes include a polymer core that changes resistance with temperature, which is a crucial material for their operation. Constant-wattage heat tapes provide a consistent level of heat regardless of environmental conditions. Although they offer simplicity in operation, they may consume more energy over extended lengths or in colder climates. High-temperature tapes, often equipped with silicone adhesive, ensure a strong attachment to pipes, facilitating efficient heat transfer in demanding environments. They're ideal for applications requiring sustained high temperatures. Combining foil-faced fiberglass wraps with heating cables enhances insulation, offering improved freeze protection and energy efficiency. This layered approach helps maintain consistent temperatures and reduces heat loss. Some heat tape systems incorporate built-in thermostats that cycle the heat ON and OFF to optimize energy consumption and maintain safe operating conditions. This feature improves overall performance and safety by preventing overheating and reducing electricity use. To further improve efficiency, advanced insulating materials are sometimes used alongside heat tapes. Understanding the materials and mechanisms behind these heat tapes enables users to select the most suitable solution for their pipe protection needs, ensuring reliable performance across diverse UK environments.
Proper Installation and Usage Guidelines
Proper installation and usage of pipe heating systems require meticulous attention to preparation, positioning, and safety standards to ensure optimal performance and prevent hazards.
First, pipes should be thoroughly cleaned and dried before applying the heat tape to maximize adhesion and heat transfer efficiency. This step helps improve the effectiveness of the heat cable. Ensuring that pipes are free of dust, grease, and moisture enhances the overall insulation performance.
Inspect pipes for leaks, and confirm that the heat tape’s plug end is near a GFCI-protected socket to minimize electrical risks.
When securing the cable, employ temperature-rated electrical tape or cable ties spaced approximately every 15 to 30 centimeters, ensuring even placement without overlaps or bunching.
For effective insulation, cover the pipe and cable with suitable material such as foam or fiberglass, snugly fitting around bends and joints.
Use weatherproof wraps for exposed systems, and always follow manufacturer instructions on connections and sensors for safety and optimal performance. Celotex insulation is an example of a high-performance thermal insulation material that can be used in conjunction with pipe wraps to enhance overall thermal efficiency.
Safety Standards and Best Practices for Electric Pipe Heating
Adherence to recognized safety standards is essential for the dependable and secure operation of electric pipe heating systems. Regulatory bodies such as the Health and Safety Executive (HSE) require electrical equipment to be designed, installed, and maintained in a manner that eliminates hazards capable of causing death or serious injury.
All heating cables must possess third-party certifications such as UL listing, CSA, or FM approval, particularly when installed in hazardous environments. Self-regulating heating cables should undergo rigorous endurance testing to ensure they retain at least 85% of their original heating power after extensive heat cycling at high temperatures, thereby affirming their reliability over time.
Installation and operational procedures must adhere strictly to comprehensive safety documentation. This includes regular inspection and maintenance practices, such as annual checks for physical damage or deterioration. Any compromised cables should be replaced immediately to prevent electrical faults or fire hazards.
Electrical ratings must be carefully matched to the specific application requirements to avert overloading. Proper installation protocols—such as avoiding overlaps, preventing direct contact with pipes, and refraining from using extension cords—are critical measures to minimize fire risks and promote long-term safety. Proper installation practices are vital to ensure compliance with safety standards and to prevent potential hazards.
Additionally, understanding how hazardous environments impact electrical safety can help mitigate risks associated with electric pipe heating systems in different settings.
Advances and Future Trends in Pipe Heating Solutions
Recent developments in pipe heating technology are fostering notable enhancements in operational efficiency, reliability, and environmental sustainability. Industry leaders are set to implement actively heated flexible pipe systems by 2025, which incorporate proprietary resistance heating within the pipe bores. These systems are specifically engineered to tackle subsea challenges such as wax and hydrate formation, thus minimising operational disruptions during energy extraction and transportation. Signed in March 2024 with an undisclosed customer, The technology employs passing electrical current through stainless steel inner carcasses, with the return current routed via metallic armour layers, functioning similarly to a coaxial cable to optimise efficiency. Such advancements are expected to deliver energy savings of approximately 50% in comparison to traditional methods. Furthermore, these systems simplify installation, maintenance, and operational processes, resulting in reduced costs. They also offer increased flexibility through targeted heating solutions, removing the necessity for additional insulation or modifications to the pipes themselves. These innovations hold the promise of rendering subsea pipeline operations more sustainable, cost-effective, and adaptable to future demands within the UK’s energy landscape. Incorporating insulation materials that are compatible with these advanced systems can further enhance their efficiency and durability over time.
Conclusion
Electric pipe wrap offers an effective solution for preventing pipes from freezing by utilising specialised heating elements embedded in durable materials. A sound understanding of its functions, installation procedures, and safety practices ensures reliable and efficient operation. Staying informed about advancements in heat tape technology can enhance system performance and longevity. Implementing industry standards and guidelines reduces risks and maximises benefits. Overall, electric pipe wrap provides a practical, dependable method for maintaining piping integrity in cold environments when used correctly and safely.