Electric Water Pipe Heat Cable
Electric water pipe heat cables are designed to prevent pipes from freezing, melt snow and ice, or maintain specific temperatures in both residential and industrial settings. They come in various types, including constant wattage and self-regulating cables, each suited to different applications.
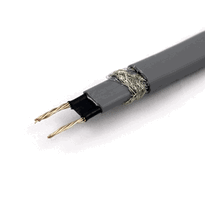
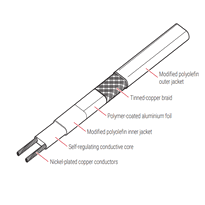
These cables are constructed from weather-resistant materials such as UV-stabilized thermoplastics or PVC, ensuring durability when exposed to outdoor conditions. The internal wiring typically consists of copper or nichrome wires, embedded within polymers that allow the cable to adjust its heat output based on temperature changes.
Operating at temperatures up to 250°C, these cables adhere to specific electrical standards and safety features to prevent hazards. Proper installation is essential for optimal performance and safety, involving suitable insulation, secure connections, and adherence to manufacturer guidelines. Regular maintenance and inspections help ensure the cables operate efficiently throughout their lifespan.
By selecting the appropriate type and ensuring correct installation, electric water pipe heat cables provide an effective solution for protecting pipes from cold weather, reducing ice-related damage, and maintaining consistent temperatures in various UK-based environments.
Types and Functionality of Electric Water Pipe Heat Cables
Electric water pipe heat cables are primarily classified into two types: constant wattage and self-regulating (self-limiting) cables. Each type is designed to meet specific needs based on their unique operational mechanisms.
Constant wattage cables deliver a fixed power output per meter, regardless of surrounding temperature changes. This ensures a consistent level of heat, making them suitable for applications that require uniform and reliable heating. They operate at a set power level and, without external control devices such as thermostats, may risk overheating if not carefully managed. This could potentially lead to damage, especially if the cable is in an environment with limited temperature fluctuation. Proper installation is essential to prevent safety hazards and ensure optimal performance. Additionally, selecting a cable with appropriate wattage is crucial to efficiently match the heat loss characteristics of the pipe and prevent energy wastage.
In contrast, self-regulating cables adjust their power output dynamically according to ambient and surface temperatures. When temperatures are colder, these cables increase their heat output, whereas in warmer conditions, they decrease it. This self-limiting behavior helps prevent overheating and promotes energy efficiency. The advanced technology behind these cables involves a polymer core embedded with conductive segments that respond to temperature changes, a process aligned with Industry 4.0 practices supporting better manufacturing precision and performance.
Such adaptive features make self-regulating cables particularly suitable for applications subject to variable external temperatures, including freeze protection of water pipes or roof de-icing.
Both types of cables are vital components in the safe and effective management of water pipe heating systems across the UK. Selecting the appropriate cable depends on the specific environmental conditions and operational requirements of each installation.
Construction Materials and Design Features
Construction materials and design features of electric water pipe heat cables are carefully engineered to ensure durability, safety, and effective performance in challenging outdoor and indoor environments. The cable jacket and outer sheath are typically made from UV-resistant thermoplastics or PVC, providing robust protection against weather exposure, mechanical wear, and moisture ingress. These materials are flexible, facilitating easy installation along pipes of various shapes and sizes, and are rated to withstand a wide temperature range from below freezing to high operating temperatures. The conductive core comprises metallic conductors such as copper or nichrome wire, with embedded self-regulating polymers that adjust heat output in response to ambient temperature changes. This self-limiting feature enhances safety and energy efficiency, preventing overheating and reducing energy consumption. Designed with insulation layers and thermal barriers, these heat cables optimize thermal performance and minimize heat loss while also preventing short circuits. Additional safety features commonly incorporated include thermostats, indicator lights, grounding devices, and self-limiting heat technology—all aimed at ensuring safe operation under diverse conditions. The materials used are also selected for their resistance to chemical corrosion and environmental degradation, ensuring long-lasting performance. Properly engineered thermal insulation maintains efficient heat transfer and minimizes energy waste. Through precise engineering of materials and thoughtful integration of safety features, electric water pipe heat cables deliver reliable, efficient, and safe heating solutions suitable for the UK's variable climate.
Operating Conditions and Electrical Specifications
The operating conditions and electrical specifications of water pipe heat cables are vital factors that influence their safe and effective performance. These cables typically operate within a temperature range of up to 250 °C, depending on their design, but generally maintain surface temperatures between just above freezing and approximately 60 °C. Ensuring proper insulation and correct installation is crucial for consistent temperature control, helping to prevent damage to pipes. The power supply requirements necessitate dedicated circuits—usually rated at 13 or 20 amps at 230 volts—with the use of circuit breakers and residual current devices (RCDs) recommended to enhance safety. Power consumption varies according to the cable length and wattage per metre, so it’s essential that circuits are appropriately rated and sized to prevent overloads. Weatherproof electrical connections, correct fixing techniques, and strict adherence to electrical regulations are fundamental to achieving reliable operation. Dedicated circuits protect freeze protection systems from interference. These measures minimize safety risks during continuous or seasonal use, ensuring the heat cables function effectively while maintaining safety standards across a range of operating conditions.
Common Applications and Environmental Uses
Water pipe heat cables are employed across a wide array of applications in diverse environments, offering targeted solutions in both industrial and domestic settings. They're critical in preventing the freezing and subsequent damage of pipelines used for water, chemicals, and petrochemicals, particularly in cold UK climates. Their purpose is to prevent water pipes from freezing in low temperatures, safeguarding the integrity of the pipeline system. These cables are also essential for household safety, being installed on outdoor taps, in basements, and within crawl spaces to ensure continuous water flow during winter months. Furthermore, they're utilized for melting ice and snow on roof gutters, downstream pipes, and external drains, thereby maintaining safety and operational efficiency. In industrial contexts, heat cables help to sustain consistent process temperatures in pipelines and complex geometrical structures, which can enhance product quality and operational reliability. The use of insulation materials such as Armaflex insulation further optimizes the efficiency of these cables by reducing heat loss. Utility providers make use of these cables to safeguard municipal water mains, reducing long-term maintenance costs and preventing costly emergencies caused by freezing or damage.
Installation Practices and Performance Considerations
Proper installation of electric water pipe heat cables is essential to ensure effective freezing protection and optimal performance.
Commence at one end of the pipe, laying the cables parallel on straight sections and spirally on bends to promote uniform heat distribution. Ensuring direct contact between the cable and the pipe surface enhances heat transfer efficiency.
Secure the cable with electrical tape or cable ties spaced approximately 30 centimeters apart, tightening the tape sufficiently without damaging the cable.
Install insulation that fully covers both the pipe and the cable, minimizing heat loss. Maintain the minimum bending radius of about 2.5 centimeters to prevent damage to the cable.
Use a properly grounded outlet, ideally with Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) protection, and avoid overloading circuits.
Regular inspections are advisable to verify that the cable adheres properly and that the insulation remains intact, ensuring consistent heating and effective freeze prevention.
Ensuring proper insulation coverage helps prevent thermal bridging and maximizes the system’s energy efficiency, improving overall performance.
Conclusion
Electric water pipe heat cables provide a dependable solution for preventing pipe freezing and ensuring continuous fluid flow in a variety of settings. Their effectiveness hinges on selecting the appropriate type, considering construction materials, and evaluating specific operating conditions. Proper installation is crucial to achieve optimal performance and maintain safety standards. A thorough understanding of electrical specifications and environmental factors enables informed application, thereby reducing the risk of damage or failure. When used and maintained correctly, these cables offer a reliable and long-lasting method to protect water systems across diverse environments in the UK.