Electrical Heat Tracing Wire
Electrical heat tracing wires are specialized cables engineered to provide controlled and uniform heating in a variety of industrial and commercial settings, such as pipelines, storage tanks, and process vessels. They are available in different types, including power-limiting, constant-wattage, and self-regulating cables, each designed to meet specific applications and performance requirements.
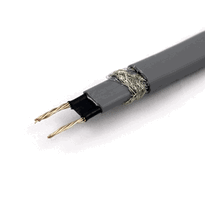
Constructed from durable materials, these cables typically feature nickel-plated copper conductors for reliable conductivity, high-temperature insulation to withstand demanding conditions, and metallic shielding to prevent electromagnetic interference. Their robust design ensures long-term performance and safety in challenging environments.
Proper installation is crucial to ensure optimal efficiency and safety. This involves adherence to specified standards, correct wiring techniques, and appropriate protective devices. Additionally, sophisticated control systems such as temperature controllers and sensors are often employed to regulate heat output, minimize energy consumption, and prevent overheating.
Understanding the fundamentals of electrical heat tracing wires—including their construction, installation procedures, and safety considerations—is essential for achieving reliable heating performance. This knowledge enables efficient operation and helps maintain safety standards in various industrial and commercial applications across the UK.
Types of Electrical Heat Tracing Wires
Are you aware that there are several distinct types of electrical heat tracing wires designed to meet different industrial and safety requirements?
Power-limiting cables feature a heat element with reduced power at crossover points, making them suitable for complex layouts where overlapping is necessary, while preventing overheating by adjusting power output based on temperature. Their resistance decreases as temperature drops, which allows for better energy efficiency and prevents overheating issues in crowded wiring setups. This feature enhances safety and minimizes fire risks in sensitive environments.
Constant-wattage cables consist of multiple zones that deliver uniform heat regardless of ambient conditions, but they can't be overlapped without risking damage.
Self-regulating cables use a conductive polymer matrix to adjust heat output dynamically, increasing efficiency and safety—particularly in environments where temperature variations are common. Reflective insulation properties further improve their thermal performance, making them versatile for various applications.
Each type is designed with specific applications in mind, ensuring optimal performance, energy efficiency, and compliance with safety standards across diverse industrial settings.
Materials and Construction of Heat Tracing Wires
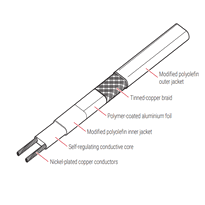
The materials and construction of heat tracing wires are fundamental to their durability, performance, and safety in industrial applications. Heat tracing wires typically feature nickel-plated copper bus conductors, often classified as 16 AWG, which ensure strong electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance—facilitating cutting to length without loss of power consistency over the entire cable. Self-regulating cables incorporate irradiation cross-linked conductive polymers over bus wires, allowing heat output to vary with temperature changes. Conductors made from nickel-chromium alloys, such as 80/20 composition, provide high-temperature stability essential for demanding environments. The insulation involves polyethylene jackets that are cross-linked to enhance heat resistance, while outer protective layers may include thermoplastic elastomers or fluoropolymers for added durability. A metallic braid, usually formed from tinned copper, shields electromagnetic interference and increases mechanical strength. Proper insulation not only prevents electrical faults but also contributes to the longevity of the cable in harsh conditions. Additionally, advances in material technology have improved the flexibility and ease of installation of modern heat tracing wires, making them suitable for complex industrial layouts.
Component |
Material |
Purpose |
| Heating core | Nickel-plated copper, NiCr alloys | Electrical conductivity, high-temperature resistance |
| Insulation | Cross-linked polyethylene | Electrical insulation, durability |
| Outer jacket/armour | Tinned copper braid, thermoplastics, fluoropolymers | Mechanical protection, corrosion resistance |
The selection of materials and construction techniques ensures that heat tracing wires meet the rigorous demands of industrial environments, providing reliable, safe, and effective performance over their operational lifespan.
Applications and Benefits in Industrial Settings
In industrial environments across the UK, heat tracing wires are essential for safeguarding operational integrity by preventing freezing and maintaining consistent temperatures in pipelines, vessels, and equipment. They ensure the uninterrupted flow of water, oils, and chemicals, particularly in colder climates, thereby avoiding damage caused by ice formation or the increase in viscosity of fluids. Heat trace cable is installed along pipes or equipment surfaces to provide heating. These systems find widespread use in sectors such as oil and gas, agriculture, water treatment, and manufacturing. Precise temperature control is crucial for safety, quality assurance, and process dependability. Heat tracing wires help in maintaining stable temperatures within processing vessels and pipelines, reducing operational downtime and lowering the risk of leaks or pipeline failure. Thermal management systems also help prevent the buildup of condensation and reduce energy consumption by precisely targeting heat where needed.
By providing accurate and controllable heat distribution, heat tracing systems support overall operational efficiency and simplify maintenance procedures. They also help in achieving compliance with safety regulations, contributing to a safer and more reliable industrial environment.
Proper implementation of heat tracing technology ensures continued productivity while prioritizing safety and long-term cost savings.
Control Systems and Safety Considerations
Control systems for electrical heat tracing wires have undergone significant advancements since their inception, evolving from basic thermostats and contactors in the 1970s to sophisticated, networked computerized controls by the 1990s. These modern systems enhance safety by precisely regulating temperature through sensors that monitor pipe or equipment heat levels, automatically adjusting power input to prevent overheating. Advanced control panels incorporate features such as system integration to enable remote monitoring and management, further improving operational efficiency and safety.
Proper matching of heat trace cables to the equipment’s heat loss is vital to avoid fire hazards. Insulation and metal jacketing further minimize heat loss and serve to protect external surfaces.
Electrical components used within these systems must meet recognized standards such as IEEE 515 and IEC 60208 to guarantee safety and reliability.
In hazardous area installations, control panels are designed to be explosion-proof, incorporating features like overcurrent protection and fault detection to ensure safe operation. These measures support the overall operational integrity and help maintain compliance with UK safety regulations.
Installation Guidelines and Compliance Standards
Installing electrical heat tracing systems requires strict adherence to established guidelines that ensure safety, efficiency, and compliance with relevant regulations.
Proper placement of the heat tracing cable begins at the circuit’s end point, preferably using isometric diagrams where available, and positioning the cable at the 4 or 8 o’clock position on the pipe. Alternative positions at the 2 or 10 o’clock may be used if accessibility issues arise.
Securing the cable involves wrapping it tightly with industrial-grade attachment tape at 30-centimeter intervals. When applying over nonmetallic piping or insulation, aluminium foil tape may be necessary to improve heat transfer and protection.
It's essential that the installation is carried out by qualified personnel, following the requirements stipulated in the British Standards and relevant electrical safety standards.
All components must be compatible and installed correctly, with thorough documentation maintained for safety, maintenance, and regulatory compliance purposes.
Adhering to these guidelines helps ensure the safe and effective operation of electrical heat tracing systems across various applications in the UK. Proper installation also minimizes the risk of improper thermal performance, which is critical for efficiency and safety.
Conclusion
Understanding the various types, materials, and control systems of electrical heat tracing wires is essential for their safe and effective application in industrial settings. Proper installation, adherence to compliance standards, and safety protocols are key to ensuring reliable operation and minimizing risks. By examining their construction and uses comprehensively, professionals can optimize energy efficiency, prevent freezing, and maintain process continuity, ultimately supporting operational safety and efficiency in diverse industrial environments.