Heat Cable
Heat cables are specialized electrical devices designed to provide controlled heating in applications such as pipe freeze prevention, roof de-icing, and floor warming. They are available in various types, including self-regulating, constant wattage, and mineral-insulated, each suited to specific requirements involving durability, energy efficiency, and safety.
Proper installation is crucial for optimal performance and safety. This involves secure placement of the cables, avoiding crossing or overlapping, and routine testing to ensure they are functioning correctly. Adhering to manufacturer guidelines and local electrical regulations is essential throughout the installation process.
Continuing will reveal detailed technical features, best practices for installation, and industry-specific applications essential for effective use of heat cables.
Types of Heat Cables and Their Applications
There are several types of heat cables, each designed for specific applications based on their unique properties and operational characteristics.
Self-regulating cables adjust their heat output according to ambient temperature, using a conductive polymer core that increases resistance as temperatures drop. This allows for adaptive control, making them ideal for roof de-icing, pipe freeze protection, and hazardous environments where precise temperature regulation is essential. Their ability to safely overlap without risking damage makes them versatile for complex installations. Additionally, their energy-efficient operation reduces electricity consumption in extended use scenarios.
Constant wattage cables deliver a fixed, uniform heat regardless of ambient temperature variations. This consistency makes them suitable for applications such as floor heating, snow melting on driveways and walkways, and frost prevention in vulnerable areas, where maintaining a steady temperature is vital.
Power-limiting cables are designed to control their maximum power output based on temperature, preventing overheating and ensuring safety. They're especially useful in industrial processes requiring precise temperature management, where over-temperature conditions could cause damage or compromise safety.
Mineral-insulated cables are highly durable with high watt density, providing reliable and long-lasting performance. These cables are typically employed in heavy-duty applications such as snow melting on large surfaces, gutter and downpipe de-icing on commercial buildings, and other environmental conditions demanding resilience over extended periods.
Advantages and Limitations of Using Heat Cables
Heat cables offer several notable advantages that contribute to their effectiveness and safety in various applications. Their self-regulating nature enables the heat output to adjust in response to ambient temperatures, thereby reducing energy waste and lowering utility costs. This feature allows for efficient heating over extensive surface areas, supporting cost-effective operation, particularly in industrial environments or large-scale settings. Effective when installed correctly, which maximizes their performance and ensures they target the intended trouble spots. Additionally, safety is enhanced because these cables automatically prevent overheating, protecting surrounding materials and users from potential hazards. Their durability and resistance to chemical and mechanical damage make them reliable for long-term use in challenging conditions. Furthermore, installation is simplified owing to their flexible design and customizable features, allowing them to be adapted to different surfaces and spaces. However, their effectiveness can diminish under extreme weather conditions, and their reliance on electrical power introduces vulnerabilities during outages. Proper installation and application are essential to maximize these benefits and ensure safe, efficient operation.
Technical Features and Performance Characteristics
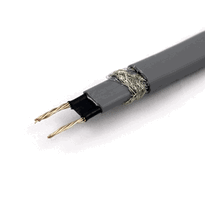
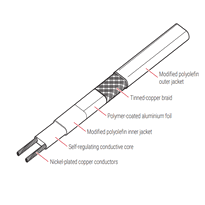
The technical features and performance characteristics of heat cables are defined by their carefully engineered construction and electrical functionality. Comprising two parallel copper bus wires embedded in a self-regulating polymeric core, these cables adjust heat output based on temperature, utilizing a semiconductive PTC polymer for self-regulation.
They're insulated with durable polyethylene jackets and protected by a tinned copper braid, which minimizes resistance and ensures safe earthing.
Rated for 230V (alternatively 120V where applicable), with power densities ranging from 0.09 to 0.63 watts per meter, these cables can operate continuously up to approximately 65°C, with peak temperatures reaching around 85°C.
Their low inrush current, resistance below 0.006 ohm per meter, and high mechanical resilience make them suitable for demanding environments.
They consistently deliver reliable heat output while resisting chemical and mechanical damage over an extended service life.
Installation Guidelines and Maintenance Tips
Proper installation of heat cables requires careful preparation of the site to ensure safety, functionality, and durability. The cable should be embedded in mortar, thinset, or concrete at a minimum ambient temperature of 5°C.
Avoid running cables beneath walls, cabinets, furniture, or appliances, as this can cause overheating and damage. Maintain at least a 25 cm distance from combustible surfaces and 30 mm from flammable materials to prevent fire hazards.
Secure cables every 1.2 meters with appropriate hold-down straps or brackets to prevent movement, and use clips fastened with silicone sealant to avoid water intrusion.
Ensure cable runs are no longer than 3 meters; for longer runs, use U-shaped loops, and avoid cutting or crossing cables.
Regularly test resistance and inspect connections to confirm safe, reliable operation over time. To support proper insulation, consider using Insulation Products and Accessories, which can help protect cables and improve energy efficiency.
Industries and Situations That Benefit From Heat Cables
Heat cables serve a vital role across a wide range of industries and applications, particularly where maintaining consistent temperatures is essential for safety, operational efficiency, and the longevity of equipment.
These specialized cables help manage thermal conditions effectively in environments subject to cold and frost.
In the industrial sector, heat cables are extensively used for pipeline heating. They help ensure the temperature of fluids remains stable inside pipelines, preventing freezing in cold weather. This not only safeguards the integrity of pipelines but also enhances process efficiency and reduces costly downtime. Designed for surface heating in challenging environments, ensuring reliable performance even in difficult industrial conditions.
Similarly, heat cables are employed to keep storage tanks at optimal temperatures, which is crucial in chemical processing and oil industries, where precise thermal control impacts product quality and safety.
Water treatment plants also benefit from the application of heat cables, as they prevent the freezing of pipes and equipment. This ensures seamless operation of water flow and ongoing treatment processes, even during severe winter conditions.
In sectors such as petrochemical, pharmaceutical, and power generation, heat cables are integral to maintaining the desired temperature of process fluids. They help support critical operations and prevent freezing-related failures, thereby ensuring continuous productivity and safety.
Construction and civil engineering projects utilize heat cables for practical purposes such as floor heating and snow melting systems. These applications improve safety and comfort by reducing slipping hazards and ensuring accessible walkways during cold spells. Energy-efficient solutions like these can significantly lower overall operational costs and environmental impact.
Such installations are particularly valuable in public spaces, institutions, and residential developments.
Emerging technological applications are also making use of heat cables to improve energy efficiency and environmental sustainability. These developments contribute to reducing overall energy consumption and promoting greener operational practices.
Overall, heat cables provide an effective and versatile solution to thermal management challenges across numerous industries.
Conclusion
A thorough understanding of heat cable types, features, and installation practices is crucial for their effective use across various industries in the UK. When selecting the appropriate heat cable, attention to technical specifications and strict adherence to maintenance guidelines can optimize performance and extend the lifespan of the product. Recognizing suitable applications and managing potential limitations are essential to prevent failures and safety hazards.
Implementing comprehensive installation procedures and undertaking regular upkeep maximize efficiency, reduce operational costs, and enhance durability. Properly maintained heat cables are a dependable solution for heating needs in diverse environments, from industrial facilities to commercial and residential settings. Ensuring that these systems are correctly specified and properly maintained safeguards safety, promotes longevity, and guarantees optimal thermal performance.