Heat Strips for Pipes
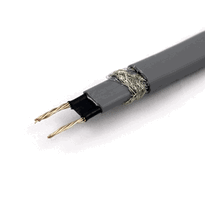
Heat strips for pipes are electrical heating elements designed to prevent freezing by providing consistent or adjustable warmth directly to vulnerable pipe sections. They function by maintaining water in a liquid state, thereby reducing the risk of expansion and pipe bursts during cold weather. Proper installation involves fixing the strips evenly along the pipe and insulating critical areas to maximize efficiency. Additionally, safety measures such as using GFCI-protected outlets are essential for safe operation. Understanding the different types and features of heat strips can enhance their effective use; continuing this guide offers further detailed insights.
Understanding How Heat Strips Protect Pipes From Freezing
Heat strips protect pipes from freezing by providing direct electrical warmth that keeps the pipe's surface temperature above the freezing point of water. They operate by emitting consistent or automatically modulated heat, depending on the ambient temperature, ensuring efficient energy use while preventing ice formation inside the pipe. When installed correctly—securely wrapped or attached along the length of the pipe—these strips create a barrier against freezing conditions. By maintaining the water inside the pipe in a liquid state, they prevent water expansion that can cause pipe bursts and costly damage. Combining heat strips with proper pipe insulation enhances freeze protection, especially during long periods of cold weather. Proper installation and regular maintenance are essential to ensure safety and effective operation, making heat strips a practical solution for preserving pipe integrity in the UK’s cold climate. Enhanced safety features help prevent electrical hazards.
Choosing the Right Heat Tape: Types and Features
Selecting the Correct Heat Tape: Types and Features
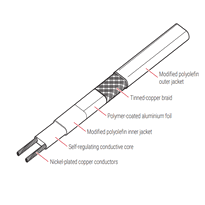
When choosing a heat tape, it’s essential to understand the different types available and the specific features that influence their performance, safety, and energy efficiency. Understanding these options ensures you select the most suitable product for your needs, whether for frost protection or maintaining consistent temperatures in challenging conditions.
Types of Heat Tape
Self-Regulating Heat Tape
This type adjusts its heat output based on the ambient temperature around it. When temperatures are low, it produces more heat; when they rise, it reduces heat output accordingly. This adaptive feature makes self-regulating tapes safer, as they are less likely to overheat, and more energy-efficient, because they only generate as much heat as needed. Their flexibility and water-resistant properties also make them popular for a variety of applications.
Constant-Wattage Heat Tape
Constant-wattage tapes deliver a steady level of heat regardless of environmental conditions. They maintain a consistent temperature, making them suitable for environments subject to constant freezing conditions. However, they tend to consume more power than self-regulating types, which can increase operational costs. While providing reliable heat, they require more careful installation to prevent overheating in specific areas.
Non-Regulating Heat Tape
Providing continuous heat irrespective of ambient conditions, non-regulating tapes are suitable only for environments where temperatures remain consistently below freezing. As they do not adjust their output, they pose a higher risk of overheating if not carefully managed. These tapes are typically used in applications where constant heat is necessary and environmental conditions are controlled.
Additional Features
Thermostats
Many heat tapes include thermostats that allow for manual regulation of temperature settings, enhancing safety and operational control.
Flexibility
Flexible designs are important for installing heat tapes around curved or awkward surfaces, ensuring even coverage and effective protection.
Water Resistance
Water-resistant or waterproof options provide added durability, particularly in outdoor or damp environments, reducing the risk of electrical issues or damage.
Energy consumption is a key consideration when selecting heat tapes, especially for long-term operational cost savings and environmental impacts.
Summary Table
| Type of Heat Tape | Key Features |
| Self-Regulating | Adaptive, energy-efficient, safer |
| Constant-Wattage | Steady heat output, higher energy consumption |
| Non-Regulating | Continuous heat, higher risk of overheating |
Choosing the right heat tape depends on your specific requirements, environmental conditions, and safety considerations. By understanding these different types and features, you can make an informed decision to ensure safety, efficiency, and durability.
Proper Installation and Safety Measures for Heat Tape
Proper installation and adherence to safety measures are essential to ensure the effective functioning and long-term safety of heat tape systems. Meticulous surface preparation involves thoroughly cleaning the pipe surface to remove dirt, moisture, or oils that could hinder heat transfer. Inspecting the heat tape itself for tears or damage helps prevent electrical hazards and ensures reliable operation. Selecting the correct heating tape based on surface geometry and environmental conditions is a crucial step before installation to guarantee optimal performance and safety. During attachment, the heat tape should be positioned evenly along the pipe, secured with electrical tape every 15 to 30 centimetres, and kept flat to avoid damage. Electrical connections must be made using a GFCI-protected socket, and thermostats or controllers should be set to regulate the heat output to prevent overheating. Proper insulation around the pipes enhances efficiency and helps to maintain consistent temperatures. Proper insulation reduces heat loss, especially at critical points such as bends or joints, and contributes to safety by preventing accidental contact with hot surfaces. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for the specific heat tape system used, and ensure that safety standards and electrical regulations are strictly observed throughout the process.
Conclusion
Proper selection, installation, and maintenance of heat strips are essential to effectively prevent pipe freezing. Understanding the differences among types and features ensures maximum performance and safety. Adhering to recommended safety procedures during installation minimizes risks associated with electrical equipment. Regular inspection and prompt adjustments improve durability and reliability, safeguarding plumbing systems in cold conditions. Implementing these practices provides a practical, long-term solution that minimizes potential water damage and energy waste caused by frozen pipes.