Heated Wire for Frozen Pipes
Heated wire systems for frozen pipes utilize self-regulating or constant wattage cables to provide controlled warmth, preventing freezing and aiding thawing efforts. Installation involves securing cables evenly along pipes, avoiding overlaps, and following manufacturer instructions while ensuring electrical safety by using appropriate earthing and circuit protection devices. These systems are designed to withstand outdoor conditions and offer energy-efficient, safe operation, reducing risks associated with freezing. Further details on installation techniques and safety precautions can help ensure optimal and reliable performance.
Understanding Heated Wire Systems for Pipe Protection
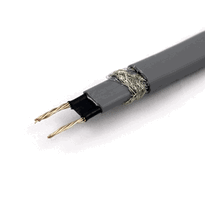
Heated wire systems are essential technologies used to prevent pipes from freezing and bursting in cold climates. Understanding how they work involves examining the different types of cables available and their operating principles.
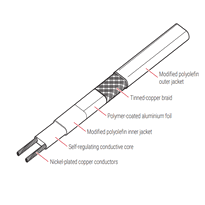
Self-regulating heating cables adjust their heat output in response to the surrounding temperature. They contain a polymer core that changes resistance as the temperature varies, allowing the cable to automatically regulate its heat. This feature prevents overheating, reduces energy consumption, and enables safe overlapping without damage—making them an efficient and safe choice for maintaining pipe temperatures above freezing. They are also designed to withstand harsh weather conditions, enhancing their durability and performance in outdoor environments.
Constant wattage cables deliver a fixed amount of heat regardless of external conditions. They generally require thermostats for temperature control to prevent overheating and ensure consistent performance. These cables are straightforward in design and suitable for applications where precise temperature regulation is less critical.
Parallel circuit cables provide uniform heat distribution along their length, making them well suited for a variety of pipe sizes and configurations. Their design facilitates even heating, which helps prevent cold spots and ensures effective pipe protection throughout the system. Proper installation of these cables requires understanding thermal regulation, to optimize energy use and safety in outdoor or uninsulated areas.
All electric heated wire systems are designed with durability in mind, capable of providing long-term protection for pipes. By selecting the appropriate type of cable based on specific installation requirements, users can ensure reliable, safe, and energy-efficient pipe heating.
Proper Installation and Safety Practices for Heated Wires
What are the essential steps to ensure a safe and effective installation of heated wire systems on pipes? First, carefully read all manufacturer instructions and safety warnings before beginning installation to fully understand the correct procedures and precautions. Select a heating cable that's suitable in length for the specific pipe. It's important to avoid using multiple cables on one pipe, as this could lead to overheating and potential safety hazards. Inspect all cables thoroughly for any damage, such as exposed wiring or compromised insulation, before installation. Damaged cables shouldn't be used under any circumstances. Plan the layout of the cable meticulously, taking into account the shape and size of the pipe. For straight sections, position the cable parallel to the pipe. When dealing with curves or bends, spiral wrapping the cable ensures even heat distribution and reduces stress on the wire. Secure the cable firmly in place using appropriate materials such as electrical tape or cable ties. Attach them every 30 centimeters (cm) along the length of the cable. Be cautious to prevent overlaps or crossings, as these can cause localized heat build-up and increase the risk of damage or fire. Ensure that the power supply complies with UK electrical standards. Always use a properly grounded electrical outlet and, where required, install a residual current device (RCD) or residual current circuit breaker with overcurrent protection (RCBO) for enhanced safety. Regularly check that all connections are secure and the system is functioning correctly during and after installation. Using proper grounding and safety devices minimizes electrical hazards and enhances system safety. Following these guidelines will help ensure your heated wire system operates safely and efficiently, providing reliable heat to your pipes.
Benefits and Limitations of Using Heated Wire for Thawing
Using heated wire systems for pipe thawing in the UK offers several notable advantages. Chiefly, they provide controlled and consistent warmth directly to the affected pipes. This targeted heating reduces the risk of hot spots or burns, allowing for gentle melting of ice and restoring water flow efficiently. Additionally, thermally controlled heat tapes are energy-efficient because they activate only when necessary, making them a cost-effective and environmentally friendly solution. Furthermore, they are a safer alternative to open flames or high-temperature devices, significantly reducing fire hazards.
However, there are limitations to consider. Proper wrapping and securing are essential to ensure even heat distribution across the pipe surface. The effectiveness of heated wire systems heavily depends on a stable power supply; interruptions can compromise the thawing process. Moreover, these systems may be less effective when dealing with inaccessible or heavily insulated pipes, where direct contact is limited or heat cannot penetrate adequately.
To maximize benefits and minimize risks, correct installation following manufacturer guidelines is vital. Regular inspection and maintenance also help ensure the system performs reliably and safely.
Benefit |
Limitation |
| Controlled, consistent warmth | Requires proper wrapping and securing |
| Energy-efficient, thermostatic control | Depends on reliable power supply |
| Safer than open flames | Less effective on inaccessible or heavily insulated pipes |
Conclusion
Heated wire systems provide an effective solution for preventing and thawing frozen pipes when correctly installed and maintained in accordance with safety guidelines. Proper installation involves precise placement of the wire, correct connection to a suitable power source, and regular inspection to ensure optimal functionality and safety. While these systems offer reliable heating, there are certain limitations to consider, including potential energy costs and the necessity for continuous monitoring during extreme winter conditions.
Overall, diligent adherence to best practices maximizes their benefits, helping to maintain pipe integrity and prevent property damage. Proper planning and regular checks are essential to ensure the system operates effectively and safely throughout the colder months.