Pipe Heating Cable
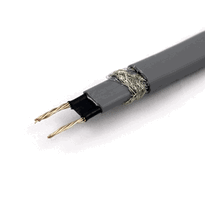
Pipe heating cables are vital for preventing freezing and maintaining consistent temperatures within pipelines. They come in self-regulating and constant wattage types, engineered with durable components such as moisture-resistant jackets and copper bus wires.
Proper installation involves measuring the length of the pipe accurately, securing the cables firmly with ties, and ensuring even coverage. Special attention should be given to areas around bends and elbows to guarantee uniform heating. Selecting the correct voltage, power output, and temperature ratings is essential to ensure safety, efficiency, and the longevity of the system.
Continuing will provide detailed guidance on optimal installation practices and system maintenance, helping you achieve reliable and effective pipe heating performance throughout the colder months.
Types and Construction of Heating Cables
What are the fundamental differences between the main types of heating cables used in various applications? Self-regulating and constant wattage cables constitute the primary categories.
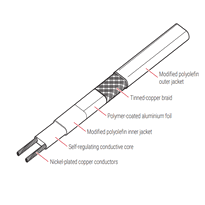
Self-regulating cables adapt their heat output according to ambient temperature. They utilize a semiconductive core that reduces resistance as it warms, enabling safe overlapping during installation without risk of overheating. These cables are typically constructed with two bus wires embedded within a polymer core, which is then coated with insulation and moisture-resistant jackets. Their intelligent design allows for energy-efficient performance and reduces the risk of thermal runaway. This design allows for efficient, energy-saving operation, making them suitable for applications such as freeze protection and pipe heating. The self-regulating feature involves electrical properties that change with temperature, enhancing safety and energy efficiency. This design allows for efficient, energy-saving operation, making them suitable for applications such as freeze protection and pipe heating.
In contrast, constant wattage cables maintain a fixed heat output regardless of surrounding conditions. They consist of parallel resistance wires made from nickel-chromium alloy, ensuring consistent performance. These cables require external control devices such as thermostats to regulate their temperature effectively.
Their construction includes insulation layers and a durable external jacket, providing robustness for demanding environments, including process heating and fire protection.
Both types are engineered for specific applications, with significant differences in operational properties and installation requirements. Self-regulating cables offer flexibility and safety benefits, while constant wattage cables provide predictable, steady heat output essential for precise process control.
Voltage, Power Output, and Temperature Ratings
Voltage, power output, and temperature ratings are essential specifications that determine the suitable application and safe operation of pipe heating cables. Accurate voltage ratings, such as 230 V, 240 V, or 250 V, ensure compatibility with UK power supplies and influence the maximum current draw.
Power output, measured in watts per meter, generally ranges from 30 W/m to 100 W/m. This affects heating efficiency and circuit planning.
Temperature ratings, with maximum continuous temperatures around 65°C and intermittent exposures up to 85°C, guide material selection and system safety standards.
In addition, understanding thermal conductivity helps optimize the insulation needed to achieve efficient heat transfer while maintaining safety.
1. Appropriate voltage ensures safe, efficient operation and prevents overloading of circuits.
2. Power output influences cable length and heat distribution to achieve desired heating performance.
3. Temperature ratings determine suitable insulation materials and application environments.
4. Adhering to these specifications guarantees system safety, compliance with regulations, and longevity of the installation.
Installation Techniques and Application Guidelines
Proper installation of pipe heating cables demands careful planning and adherence to detailed procedures to guarantee safety, efficiency, and long-term performance. Precise measurement of pipe length, inspection for sharp bends, and verification of pipe diameter are essential initial steps. Selecting compatible cables and thoroughly cleaning the pipe surface improve contact and adhesion, ensuring the system’s reliability. Verify that the cable’s power output matches the heating requirements for your pipe size and conditions to prevent inefficiency or damage. Additionally, choosing robust enclosure options helps protect connections in challenging environments.
Step |
Key Consideration |
| Cable Placement | Maintain uniform spacing along straight sections; spiral on irregular bends |
| Securing Cables | Use ties every 30 centimetres; avoid overtightening to prevent damage |
| Insulation Post-Installation | Fully cover the cable, especially around elbows, with snug insulation |
| Electrical Connections | Leave extra cable length at connection points; test for continuity and insulation resistance |
Adhering to these guidelines ensures effective heat transfer, a secure attachment, and compliance with safety standards. This is fostering a reliable heating system built for durability and peace of mind.
Environmental Resistance and Safety Features
The environmental resistance and safety features of pipe heating cables are carefully engineered through the selection of specialized materials and construction techniques designed to withstand harsh conditions and ensure dependable operation.
1. Heating cables utilize nickel- or tin-plated copper bus wires embedded within a self-regulating polymeric core. This design manages power output effectively and allows safe application on both plastic and metal pipes.
2. The outer jackets are manufactured from chemically resistant polyolefin or fluoropolymer materials, providing protection against chemical attack and mechanical damage. Layers of Teflon® or Kapton® further enhance resistance to moisture and chemicals, increasing durability.
3. Tinned copper braids serve as grounding points and provide additional protection against environmental factors. Their resistance levels are verified according to recognised standards such as ASTM or IEEE.
4. Elastomeric insulation layers, such as those made from EPDM, minimise moisture ingress, thereby improving durability and safety during prolonged use in challenging environmental conditions.
Conclusion
Proper selection, installation, and maintenance of pipe heating cables ensure reliable performance and safety. Understanding the different types and their construction helps in choosing the appropriate cable for specific applications, while awareness of voltage, power output, and environmental resistance allows for optimal functioning. Following established guidelines minimises risks and guarantees efficient heating. By adhering to these detailed technical principles, users can achieve long-lasting, safe, and effective pipe heating solutions in various operational environments.