Pipe Heating Wire
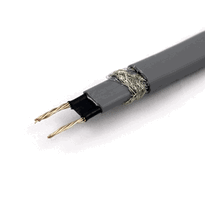
Pipe heating wires are specialized electrical cables designed to prevent pipes from freezing and to maintain consistent temperatures in various environments, including industrial, commercial, and residential settings. These wires are available in different types, such as self-regulating, constant wattage, and mineral-insulated, each offering unique features suited to specific applications.
Typically made from flexible conductors like copper or advanced alloys, these wires enable customization in installation and facilitate effective heat transfer. Proper utilization involves careful positioning along the pipe, securing the wires at regular intervals to ensure even heat distribution, and integrating sensors to monitor temperature and enhance safety.
Understanding the correct installation techniques and selecting the appropriate type of wiring are essential for creating efficient, safe pipe heating solutions. When applied correctly, pipe heating wires provide reliable performance while helping to prevent pipe freezing and related damages.
Types of Pipe Heating Wires and Their Applications
There are several types of pipe heating wires designed to suit a range of applications, each distinguished by their construction, heat output characteristics, and suitability for specific environments.
Self-regulating wires adapt their heat output dynamically based on ambient temperatures. This feature prevents energy wastage and reduces the risk of overheating, making them particularly suitable for freeze protection on residential and light commercial water pipes. They’re ideal in areas with variable temperatures, offering flexibility for installations around bends, valves, and other irregular pipe sections.
Constant wattage wires, on the other hand, provide a fixed heat output per unit length. Such wires are well-suited for industrial applications where consistent temperature control over longer pipe runs is essential, ensuring reliable performance across extensive sections. They provide a continuous and predictable level of heat, which is critical for maintaining process integrity in industrial settings.
Mineral insulated wires feature robust sheaths that can withstand extreme conditions. These are suitable for long-term high-temperature maintenance in challenging industrial environments, offering durability and high safety standards.
Each type of pipe heating wire plays a crucial role in delivering effective and reliable heating solutions, tailored to meet specific operational requirements while maintaining energy efficiency and safety standards across diverse settings in the UK.
Key Features and Installation Considerations
Proper attachment and spacing of pipe heating wires are essential for achieving reliable and efficient heating performance. Correct installation involves positioning the heat cable at one end of the pipe, running it parallel along the lower half for straight pipes, or wrapping it spirally with evenly spaced loops for curved or large-diameter pipes.
Maintaining direct contact between the cable and pipe enhances heat transfer, helping to prevent freezing.
Securing the cable every 30 centimeters with suitable materials, such as fiberglass or aluminium tape, prevents movement and potential damage.
Insulation should fit snugly around both the pipe and the cable, particularly at bends and joints, to optimize heat retention.
Proper installation reduces energy consumption and ensures a uniform temperature across the system.
This careful method of installation not only provides effective freeze protection but also extends the longevity of the piping system, ensuring reliable operation over time. High thermal conductivity of the cable and insulation system is crucial for maximizing efficiency.
Operating Principles and Safety Measures
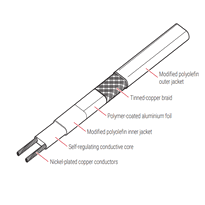
Operating principles of pipe heating wire systems are based on the conversion of electrical energy into heat through carefully designed mechanisms, ensuring efficient temperature maintenance and optimal energy use. Heat trace cables function by conducting heat directly to the surface of pipes, preventing freezing or maintaining specific process temperatures. Utilize heat conduction to transfer heat effectively. There are two main types of these cables: constant wattage cables, which deliver a steady level of heat output, and self-regulating cables, which automatically adjust their heat output according to the ambient temperature driven by a conductive polymer core. Safety measures are crucial in the design and operation of these systems. They include thermostat-controlled circuits to regulate temperatures precisely and alarm systems that alert operators to faults or system failures. Proper insulation around the cables helps minimize heat loss and enhances overall safety, while the use of surface-mounted temperature sensors ensures precise control of heating elements, preventing overheating. Installation must follow strict guidelines to ensure safety and effectiveness. These guidelines include maintaining straight runs of cable, avoiding overlaps, and using protective coverings or conduits to prevent mechanical damage. Follow installation electrical safety protocols that are thoroughly applied, with grounding of the system, appropriate circuit protection such as residual current devices (RCDs), and adherence to relevant standards to minimize risks and ensure reliable operation.
Thermal Performance, Efficiency, and Cost Factors
The thermal performance, efficiency, and cost factors of pipe heating wire systems are closely linked components that greatly influence their overall effectiveness and operational expenditure. Achieving high thermal performance often involves innovative insulation strategies, such as pipe-in-pipe designs that utilize dry insulation materials. These specialized insulations minimize heat loss, thereby enhancing energy efficiency and typically achieving efficiencies in the range of 90-95%. Electrically Heat-traced pipe-in-pipe systems incorporate high-performance dry insulation to reduce heating needs and improve overall system performance. Self-regulating cables further boost efficiency by automatically adjusting their heat output according to the pipe’s temperature, which helps to cut down on unnecessary energy consumption. Proper insulation not only ensures a stable temperature is maintained within the pipe but also reduces the long-term costs associated with energy and additional insulation materials. While these advanced insulation options may involve higher initial investments, they often result in significant savings over the system’s lifespan. Design considerations, including precise calculations of heat loss and the selection of suitable insulation materials, are vital for optimizing system performance and managing costs effectively. Utilizing sophisticated insulation solutions and pipe-in-pipe configurations enhances heat retention and overall energy efficiency. Self-regulating cables, by responding to temperature changes, further contribute to reduced power consumption. Additionally, insulation quality plays a crucial role in preventing heat dissipation and maintaining system reliability, especially in challenging weather conditions. Balancing initial costs with long-term operational savings requires careful planning and customized system design. By selecting appropriate insulation materials and system configurations, users in the UK can ensure their pipe heating systems operate efficiently, cost-effectively, and with minimal heat loss, thereby supporting sustainable and economical infrastructure management.
Advantages and Limitations of Different Heating Cable Options
Different heating cable options offer a range of advantages and limitations that influence their suitability for various piping applications. Heat tape is highly flexible, making it ideal for wrapping irregular or complex pipe shapes. However, it requires precise application to prevent overheating and potential failure.
Heat trace cables are slightly stiffer, yet still pliable enough for wrapping around straight or gently curved pipes. They can be cut and customized to fit specific lengths, enhancing installation flexibility. Unlike heat tape, heat trace cables can be more easily integrated into automated control systems for temperature regulation.
Heating cords share similar flexibility but are typically supplied in fixed lengths, which may limit adaptability.
Self-regulating cables automatically adjust their output, reducing the risk of overheating and increasing safety. This makes them suitable for sensitive environments.
Constant wattage options, on the other hand, require external controls to prevent thermal damage, which can add to installation complexity.
Conclusion
Selecting the appropriate pipe heating wire requires careful consideration of type, installation method, safety protocols, and thermal efficiency. Understanding the specific application and the advantages and limitations of each option ensures maximum performance and cost-effectiveness. Proper installation, adherence to safety standards, and regular maintenance are essential to maintain reliable operation. Ultimately, informed decision-making based on detailed technical knowledge is vital for effectively preventing pipe freeze damage and ensuring energy-efficient heating systems.