Water Pipe Heat Wrap
Water pipe heat wraps are insulating materials designed to reduce heat loss and prevent freezing in cold environments. Common options include foam insulation made from polyethylene or elastomeric foam, which offers flexibility, moisture resistance, and ease of installation, especially suitable for cold water pipes. Proper application involves thorough pipe surface cleaning, selecting compatible materials, and ensuring a secure fit and electrical safety during installation. Continuing, it is essential to consider how to optimise insulation for energy efficiency and effective maintenance.
Types of Water Pipe Heat Wrap Materials
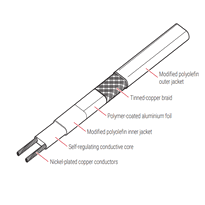
Water pipe heat wraps utilise various materials, each offering unique properties tailored to different insulation needs and environmental conditions. Foam pipe insulation, typically manufactured from polyethylene or elastomeric foam with a closed-cell structure, delivers excellent thermal insulation, flexibility, and ease of installation. This makes it especially suitable for cold water pipes and applications at lower temperatures. It is also resistant to moisture infiltration, which helps prevent mold growth. Foam insulation's cost-effective nature makes it a popular choice for many residential and commercial pipe insulation projects. Fiberglass pipe insulation, composed of spun glass fibres, is capable of withstanding high temperatures and resisting corrosion. It's often employed in hot water systems or high-temperature environments, frequently complemented by vapour barriers or foil facings to enhance performance. Rubber pipe insulation, made from natural or synthetic rubber with a cellular, closed-cell design, provides high flexibility, moisture resistance, and effective thermal insulation for both hot and cold water pipes. The versatile nature of these materials ensures that the correct choice can be made based on specific environmental and operational requirements.
Enhancing Energy Efficiency with Pipe Insulation
Proper pipe insulation plays a vital role in boosting energy efficiency by reducing heat loss during the movement of hot water through piping systems. This minimisation of heat escape can be as high as 90%, leading to substantial conservation of thermal energy. The advantages are most noticeable when hot water is used at intervals of 10 to 30 minutes, as insulation helps retain heat more effectively during these periods.
Pipes situated in colder, unconditioned spaces such as crawl spaces or exposed environments tend to experience greater heat loss, making insulation particularly valuable in these locations. In fact, uninsulated pipes in cold climates are prone to freezing, which can cause expensive damage and service interruptions. is essential for maximizing performance and durability, especially in varying environmental conditions.
Metal pipes generally transfer heat more rapidly than plastic pipes, highlighting the importance of choosing appropriate insulation materials tailored to specific pipe types.
Implementing effective insulation not only reduces fuel consumption but also enhances system performance, thereby contributing positively to environmental sustainability.
Properly insulated pipes support overall energy efficiency, resulting in cost savings and improved operational effectiveness for both residential and commercial systems.
Proper Installation and Protective Measures
Before installing heat wrapping materials, it's essential to carefully inspect the pipes for any signs of leaks, damage, or weakness, as these issues can compromise the effectiveness of the insulation and pose safety risks such as electrical shorts or water damage. Addressing potential problems beforehand helps ensure the longevity and safety of your pipe system.
Clean the surface of the pipes thoroughly to ensure that heat tape adheres properly and that the insulation materials are securely fitted. Proper Pipe surface preparation is crucial for achieving optimal insulation performance and preventing issues during operation.
Avoid installing heat wraps on pipes that already show signs of damage or corrosion, as this could lead to further deterioration or failure. Use only undamaged heat wrapping materials suitable for the type of pipe—whether plastic or metallic.
Confirm that the power supply is compatible and easily accessible, ideally using a GFCI-protected outlet for increased safety. Begin the installation at the power plug end near the outlet, following proper wrapping techniques to ensure even heat distribution and secure insulation.
Conclusion
Selecting suitable water pipe heat wrap materials, ensuring correct installation, and implementing protective measures are vital steps to optimise energy efficiency and prevent damage. Understanding the properties and application methods of various wraps enables custom solutions tailored to specific infrastructure requirements. Following comprehensive installation guidelines helps minimise heat loss and exposure risks, thereby extending the lifespan of pipes. By adhering to these practices, you ensure reliable and energy-conscious performance. Possessing thorough knowledge and executing precise installation are crucial for effective pipe insulation management across UK infrastructure projects.