Types of Flat Roof Insulation Materials
There are several common materials used for flat roof insulation, each with specific properties that influence their suitability for different roofing applications.
Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) is made from expanded polystyrene beads, offering decent thermal insulation but with a lower K-value compared to other options. It's lightweight, durable, and affordable, making installation straightforward as it’s easy to cut and position. Its thermal performance makes it suitable for warm flat roofs, but it is less effective in cold conditions.
Extruded Polystyrene (XPS) features low water permeability and higher thermal resistance than EPS, making it suitable for various conditions. However, it can be affected by environmental factors such as UV exposure if not properly protected.
Mineral wool is composed of natural or synthetic fibres, providing effective insulation and added fire resistance. However, it can attract moisture without appropriate protection.
These materials form the foundation of practical, effective flat roof insulation systems tailored to specific needs, ensuring thermal efficiency, durability, and safety in a variety of roofing scenarios.
Key Features and Benefits of Polyisocyanurate (PIR) Insulation
Polyisocyanurate (PIR) insulation is recognised for its outstanding thermal performance, making it a preferred choice for flat roofing projects across the UK where efficiency and space optimisation are essential. Its high thermal resistance per millimetre allows buildings to meet or surpass the required insulation standards while employing less material and conserving roof space, resulting in more functional and cost-effective roof designs.
Furthermore, PIR maintains its thermal properties over time owing to its closed-cell structure, which effectively resists moisture absorption. This long-term stability ensures sustained insulation performance, reducing the risk of degradation. Its closed-cell structure also makes PIR highly resistant to moisture penetration and vapor passage, which is crucial in preventing issues related to condensation and water damage.
Its moisture-resistant qualities also minimise the potential for mould growth and structural damage by limiting vapour permeability, thereby enhancing the overall durability of the roof system.
Importantly, PIR offers excellent fire resistance, capable of withstanding high temperatures without melting or dripping. This characteristic significantly contributes to building safety and enables compliance with strict fire safety regulations in the UK.
In addition to its thermal advantages and safety benefits, PIR provides long-lasting durability, straightforward installation processes, and potential energy savings. These features collectively make PIR insulation a practical and effective solution for flat roof insulation systems across the UK.
Advantages of Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) and Extruded Polystyrene (XPS) Solutions
Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) and Extruded Polystyrene (XPS) are two widely utilised insulation materials whose specific properties make them suitable for various flat roof applications.
EPS offers excellent thermal insulation with a thermal conductivity typically between 0.030 and 0.035 W/m·K. In contrast, XPS provides higher thermal resistance, approximately 0.029 to 0.033 W/m·K, leading to greater energy savings. Both materials help to reduce heating and cooling costs by maintaining stable indoor temperatures throughout the year.
XPS’s closed-cell structure delivers superior moisture resistance, with water absorption rates as low as 0.3%. This makes it ideal for inverted roof systems and foundation applications where moisture management is critical. XPS’s high compressive strength, often exceeding 300 kPa, also contributes to its suitability for load-bearing applications.
Both materials are lightweight and durable, with XPS demonstrating high compressive strength, often exceeding 300 kPa. This ensures long-term stability under load.
Additionally, these materials are fire-resistant and environmentally resilient, providing?? in a variety of climates and building conditions.
Their recyclability supports sustainable construction practices, contributing to environmentally responsible building solutions.
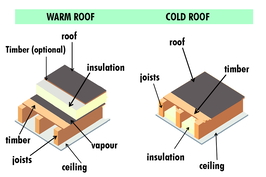
Regulatory Considerations and Best Practices for Installing Flat Roof Insulation
Regulatory Considerations and Best Practices for Installing Flat Roof Insulation
Compliance with regulatory frameworks and adherence to best practices are essential in ensuring the safe, effective, and legally compliant installation of flat roof insulation. Building regulations such as the UK Building Regulations Part L specify minimum thermal performance standards, often expressed through U-values.
Local climate zones significantly influence insulation requirements, with specific U-value targets depending on the geographic location and exposure levels. Incorporating vapour barriers correctly prevents moisture accumulation within the roof assembly, safeguarding the insulation's performance and the roof’s durability.
Proper installation involves selecting suitable insulation materials with adequate thermal properties, ensuring sufficient thickness to meet U-value requirements, and applying moisture management techniques effectively. Regular inspections and maintenance are vital to ensure the integrity of the insulation system over time and to maintain ongoing compliance with relevant standards.
To achieve optimal results, it's imperative to understand and comply with local building codes and standards before installation. Selecting insulation materials that meet or exceed the specified U-values ensures energy efficiency and regulatory compliance.
Implementing vapour barriers correctly, coupled with regular maintenance, helps prevent moisture-related issues that could compromise the insulation's performance and the longevity of the roof assembly. Understanding local regulations is crucial for ensuring the insulation system meets all legal requirements and standards.
Conclusion
Selecting appropriate flat roof insulation requires understanding material properties, regulatory standards, and installation best practices. Polyisocyanurate offers high thermal efficiency, while EPS and XPS provide durable, moisture-resistant solutions. Proper installation ensures energy efficiency, structural integrity, and compliance with building regulations. By carefully evaluating these factors, builders and property owners can achieve optimal insulation performance, extend roof lifespan, and reduce energy costs. It is essential to adhere to industry guidelines to ensure safe, effective, and long-lasting insulation systems.