Moisture Resistant Insulation
Moisture resistant insulation comprises materials such as fibreglass, mineral wool, rigid foam boards, and closed-cell spray foam, all engineered to inhibit water absorption and prevent mould growth. These insulation options deliver essential benefits, including the maintenance of thermal performance, functioning as air barriers, and safeguarding structures from damage stemming from excess moisture.
When selecting insulation, it is crucial to consider factors such as moisture tolerance and the suitability for specific environments. Exploring these materials further reveals how each type can effectively cater to diverse building requirements.
By prioritising moisture resistance in insulation choices, homeowners and builders can ensure long-lasting performance and enhanced comfort in their properties.
Common Types of Moisture Resistant Insulation Materials
Moisture-resistant insulation materials are crucial for safeguarding buildings in regions with high humidity or moisture exposure.
Fibreglass insulation is widely used due to its ability to resist water retention and prevent mould growth, making it ideal for damp conditions. However, it often requires an additional vapour barrier to enhance moisture control, as it doesn't come with one built in.
Cellulose insulation, crafted from recycled paper and treated with boron, offers a tight seal that minimises air leaks and limits moisture infiltration. It's essential, however, to ensure proper installation, as improper application can lead to moisture absorption.
Mineral wool, produced from recycled slag and rock, is naturally fire-resistant and doesn't absorb water, providing outstanding durability and stability in moist environments.
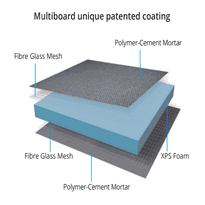
Rigid foam boards, such as extruded polystyrene (XPS), deliver excellent moisture resistance while retaining their insulating properties over time.
Proper installation of moisture-resistant insulation is vital for maintaining a healthy and efficient building, particularly in areas susceptible to moisture-related issues.
Benefits of Using Moisture Resistant Insulation
Using moisture-resistant insulation presents numerous significant advantages for building safety and efficiency. It effectively prevents water from infiltrating walls and crawl spaces, thereby reducing the risk of mould and mildew growth that can adversely affect health. Impermeable to water, materials such as closed-cell spray foam are impervious to water and don't absorb moisture, even in the event of flooding, ensuring dependable protection. This type of insulation also retains its excellent thermal performance over time, leading to reduced energy costs by minimising heat transfer. Moreover, moisture-resistant insulation serves as an air barrier, curtailing drafts and enhancing indoor air quality. It reinforces structural components and extends the lifespan of the building, which in turn diminishes maintenance and repair costs.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Insulation for Damp Environments
Choosing the right insulation for damp environments necessitates a thorough assessment of its moisture resistance to avoid issues such as water damage and mould growth. Moisture tolerance is a key factor, as it indicates how well insulation withstands exposure to moisture without degrading or losing its insulating properties. It's essential to ensure compatibility with existing materials, as certain types of insulation perform more effectively with specific construction components, which can influence overall efficiency. Taking these factors into account guarantees that the insulation will adequately protect the area from moisture while ensuring long-lasting durability. It's vital to select insulation that not only meets these requirements but also contributes to a comfortable and healthy living environment.
Moisture Resistance Level
The level of moisture resistance in insulation materials is crucial when selecting the appropriate type for damp environments. These materials vary in their ability to block or permit moisture movement. For example, vapor impermeable options effectively keep moisture at bay, while semi-impermeable choices allow for limited diffusion. It is also essential to choose the right vapour retarder; improper placement can lead to trapped moisture and encourage mould growth. FOAMGLAS cellular glass insulation, which is completely waterproof and vapour tight, is especially suitable for harsh, moisture-prone conditions, providing reliable long-term performance.
To facilitate understanding, here is a comparative overview:
Material Type |
Moisture Resistance Level |
Best Use Case |
| FOAMGLAS® | Completely waterproof, vapour tight | High moisture areas |
| Fibreglass | Low water retention | Humid environments |
| Rigid foam boards | High vapour barrier capacity | Cold climate insulation |
| Mineral wool | Moderate, requires detailing | Damp conditions |
| Cellulose (treated) | Improved moisture resistance | General damp areas |
Making the right selection ensures durability and comfort in moist settings.
Compatibility With Existing Materials
Compatibility with existing materials is a crucial factor in selecting insulation for damp environments, as various building components interact in ways that can influence overall performance.
Roofing materials, such as asphalt shingles and metal, have specific installation requirements that affect the choice of insulation, ensuring they work together effectively.
Adhesive bonds, like pressure-sensitive tapes, must be compatible to secure insulation properly, particularly in fluctuating temperatures.
Moreover, insulation materials should be resistant to chemicals, UV rays, and moisture to prevent degradation over time.
Vapour permeability is essential, as it allows moisture to escape and helps prevent mould growth.
Properly matching insulation to existing structures is vital for maintaining durability and energy efficiency.
The thermal properties of insulation should align with the climate zone to optimize energy conservation and prevent issues related to moisture buildup.
When compatibility is carefully considered, the result is a more reliable and long-lasting building that's well-suited to damp conditions.
Comparing Performance and R-Values of Moisture Resistant Options
Moisture-resistant insulation options differ considerably in their thermal performance, primarily assessed by R-values.
Polyisocyanurate (Polyiso) insulation boasts the highest R-value, making it the most energy-efficient rigid foam available. Polyiso's high R-value is achieved through a special foil facing that enhances its insulating properties. Extruded Polystyrene (XPS) offers a solid balance of durability and moisture resistance, while Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) presents moderate performance but requires additional protection in damp environments.
Closed-cell spray foam typically provides excellent insulation alongside moisture control by acting as a vapour barrier. On the other hand, traditional fibreglass batts tend to have lower R-values and can absorb moisture, which diminishes their effectiveness.
When selecting the appropriate insulation, it's crucial to consider both the required thermal performance and the material's ability to resist moisture in various settings. This informed choice can significantly enhance the energy efficiency and durability of your building.
Ideal Applications for Different Moisture Resistant Insulation Types
Different moisture-resistant insulation materials are suited for specific applications, depending on the environment and performance requirements.
Polyisocyanurate (Polyiso) is ideal for installation beneath slabs due to its high strength and capacity to remain dry under concrete. Additionally, Polyiso offers excellent thermal resistance which helps in maintaining indoor temperature stability. High strength and a closed-cell structure make it particularly suitable for below-ground use.
Extruded Polystyrene (XPS) is frequently used beneath floors and in below-grade applications, offering durability and moisture resistance in damp conditions. XPS also maintains its insulating properties even when exposed to moisture over time, which makes it a reliable choice for long-term performance.
Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) is appropriate for underfloor areas because of its lightweight nature and effective heat transfer limitation. Its cost-effectiveness and ease of installation have made EPS a popular choice in residential projects, especially in areas with moderate moisture exposure.
In wet environments such as swimming pools and spas, FOAMGLAS® cellular glass provides complete waterproofing, ensuring consistent performance over time. FOAMGLAS® is also highly fire-resistant and resistant to mold, making it suitable for highly humid or water-prone environments.
Closed-cell spray foam and blown-in insulations are effective for use within walls, ceilings, and crawl spaces, helping to prevent mould and moisture accumulation. These materials also improve air sealing, which enhances overall energy efficiency and indoor comfort.
Each type of insulation plays a specific role, ensuring the most suitable solution for every moisture-prone area.
Environmental and Safety Aspects of Moisture Resistant Insulation
Environmental and safety considerations are crucial when selecting moisture-resistant insulation materials. Natural options such as wool and cellulose excel in moisture management and effectively prevent the growth of mould and mildew. This contributes to a healthier indoor environment. Natural insulation materials also tend to have lower embodied energy, making them more sustainable choices. These eco-friendly materials also help reduce indoor allergens through their non-toxic, low-dust components, thereby enhancing respiratory health and minimising skin or eye irritation. Furthermore, they significantly reduce harmful volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emitted from synthetic insulations, leading to improved indoor air quality. In addition to their health benefits, green insulation plays a vital role in balancing humidity levels within homes, which can diminish the risk of structural damage caused by excessive moisture. Choosing environmentally responsible insulation not only fosters a healthier living space but also lessens the environmental footprint by decreasing energy consumption, lowering greenhouse emissions, and promoting sustainability through their recyclability and durability.
Conclusion
Moisture resistant insulation provides numerous advantages, making it particularly suitable for environments that are prone to dampness. Selecting the appropriate type hinges on factors such as thermal performance, application, and safety considerations. Various materials excel in specific conditions, so understanding their characteristics is essential for making informed decisions.
Overall, opting for the right moisture resistant insulation enhances energy efficiency, mitigates damage, and guarantees long-lasting durability in moisture-prone areas. A thorough evaluation leads to improved insulation solutions and greater comfort in spaces affected by humidity.