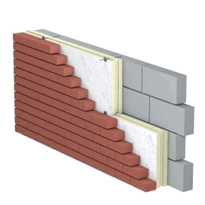
Rolled Insulation
Rolled insulation comprises a variety of materials, including fiberglass, mineral wool, natural fibers, reflective foil-backed types, and synthetic fibers. Each type is suited to specific applications such as walls, floors, ceilings, attics, basements, and crawl spaces.
This form of insulation offers effective thermal resistance and soundproofing by reducing heat transfer and noise transmission. The choice of material influences the overall performance, cost, and environmental impact of the insulation. For instance, some products contain recycled content, making them more environmentally friendly, while manufacturing methods can also vary.
Understanding the different options available helps ensure proper installation, which is essential for enhancing energy efficiency and building performance. Whether insulating a loft, lining a basement, or lining cavity walls, selecting the appropriate rolled insulation is key to creating a comfortable, energy-efficient property.
More detailed information on specific types and their benefits can assist homeowners and builders in making informed decisions tailored to their needs.
Types and Materials of Rolled Insulation
Rolled insulation includes a range of materials designed to enhance thermal efficiency and acoustic performance within buildings. Each type has distinct properties suited to different applications and environments.
Fiberglass insulation is the most prevalent choice. Made from recycled glass, it traps heat within tiny pockets to reduce heat transfer. It's cost-effective and offers straightforward DIY installation, making it a popular option for homeowners and small-scale projects.
Mineral wool insulation, produced from natural stone or slag, provides superior fire resistance and excellent soundproofing qualities. Its durability makes it suitable for commercial buildings and areas where safety is a priority.
Natural fiber options, such as sheep’s wool and cotton, are environmentally friendly alternatives. These materials offer good thermal properties and naturally help regulate moisture levels in buildings. However, they tend to be more expensive than synthetic options.
Reflective foil-backed rolls feature a reflective layer that effectively logs radiant heat. Although primarily used in warmer climates, they can contribute to energy efficiency by reflecting heat away during hotter months.
Synthetic plastic fiber insulations are less common but are available in flexible batt forms. They can provide versatile insulation solutions for various spaces, though their use is often dictated by specific project requirements.
An additional benefit of high-quality rolled insulation is its ability to prevent pipe condensation, helping maintain a dry and healthy indoor environment. Understanding the properties and suitability of these different rolled insulation materials can help ensure optimal thermal performance and safety in UK buildings.
Common Applications and Installation Techniques
Because of their versatility and ease of handling, rolled insulation materials are widely employed in various areas within both residential and commercial structures. They're commonly used in large, unobstructed spaces such as floors and ceilings, where continuous lengths simplify installation. Attics are ideal locations, allowing the insulation to be rolled out between rafters to improve thermal resistance and reduce heat loss. They're also frequently installed in walls, fitting snugly between studs to enhance thermal performance and contribute to overall home comfort. In basements, rolled insulation helps regulate temperature and minimize moisture issues, while in floors and crawl spaces, it reduces heat loss from heated areas. Its flexibility and straightforward installation procedures make rolled insulation suitable for energy-efficient construction and renovation projects across different building types. Additionally, rolled insulation is often chosen because it provides seamless coverage, reducing gaps that can lead to thermal bridging and energy loss.
Thermal and Acoustic Benefits
Thermal and acoustic benefits are key considerations when selecting rolled insulation materials for construction and refurbishment projects in the UK. These materials effectively reduce heat transfer through conduction and radiation, helping to maintain consistent indoor temperatures. They support energy efficiency by enabling thermostats to operate more effectively, which in turn reduces the workload on heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems. The thermal conductivity of mineral wool rolls remains stable over time owing to their durable fiber structure containing only atmospheric air. Furthermore, many available options feature various thermal resistance metrics, such as K-values ranging from approximately 0.035 to 0.045 W/m·K, allowing for customized thermal performance tailored to specific applications.
Benefit Type |
Explanation |
Impact |
| Thermal insulation | Reduces heat transfer via conduction and radiation | Helps maintain comfortable indoor temperatures |
| Acoustic absorption | Absorbs airborne sound waves to limit noise transmission | Promotes a quieter indoor environment |
| Multi-functional use | Offers both thermal and acoustic benefits in a single product | Enhances space utilisation and installation efficiency |
Cost, Environmental Impact, and Sustainability
Cost, environmental impact, and sustainability are vital considerations when selecting rolled insulation materials in construction projects across the UK.
The initial purchase price of rolled glass fiber insulation typically falls between £0.30 and £1.20 per square meter, making it an accessible option for many budgets. Its straightforward installation, which involves unrolling and cutting to size, helps keep labor costs minimal and speeds up project timelines.
From an energy efficiency perspective, the thermal resistance provided by glass fiber insulation contributes to reduced energy consumption for heating and cooling, enhancing its overall cost-effectiveness over the lifespan of a building.
While producing glass fiber insulation involves energy-intensive processes that release moderate levels of CO?, industry efforts are underway to reduce emissions. These include upgrading to more efficient heating systems during manufacturing and adopting renewable energy sources. Manufacturing processes are continually improving to lower the carbon footprint of insulation materials.
Sustainability-wise, the partially recycled content of glass fiber insulation supports environmental goals, though disposal remains challenging due to its non-biodegradable nature. Recycling efforts are ongoing to find more sustainable disposal options for end-of-life materials.
When properly installed, rolled fiber insulation not only helps cut down on energy use but also boosts indoor air quality and building durability, further supporting sustainable building practices.
Conclusion
Rolled insulation provides versatile options suitable for a range of construction requirements, offering effective thermal and acoustic insulation when carefully selected and properly installed. Understanding the different materials, applications, and installation techniques ensures optimal performance and energy efficiency.
When choosing rolled insulation, it is important to consider factors such as cost, environmental impact, and sustainability. These considerations help in making informed decisions that align with both budget and ecological responsibilities.
Applying precise installation methods and selecting appropriate materials can significantly enhance the insulation's effectiveness and longevity. Proper installation not only improves thermal performance but also reduces issues such as draughts and heat loss.
Overall, rolled insulation is a practical and reliable choice for improving building comfort and reducing energy costs across residential, commercial, and industrial structures.