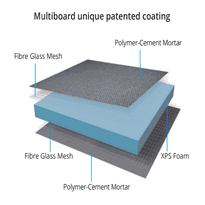
Waterproof Wall Insulation
Waterproof wall insulation is essential for protecting buildings against moisture and water damage while enhancing thermal performance. Commonly used materials include polyurethane, cementitious coatings, bituminous membranes, foam panels, mineral wool, and cellular glass. The selection of insulation materials is influenced by the specific environment, with certain options providing superior water resistance and thermal efficiency.
Proper installation of vapour barriers and effective moisture management is crucial in preventing mould growth, ensuring the longevity of the building structure. For comprehensive advice on choosing and applying the most suitable waterproof insulation, continue to explore this vital subject.
Types of Waterproof Wall Insulation Materials
There are various types of waterproof wall insulation materials available, each tailored to meet specific requirements and environments.
Polyurethane-based insulation offers excellent water resistance, safeguarding concrete from absorption. It's highly durable and provides a prolonged service life, despite being on the pricier side. Polyurethane insulation also resists mold growth(which is crucial in humid climates), making it a reliable choice for long-term protection.
Cementitious waterproof coatings serve as protective layers rather than traditional insulations. They're straightforward to apply to different surfaces; however, their inflexibility can limit certain applications.
Bituminous membrane insulation, typically available in rolls, creates a dependable moisture barrier, making it particularly effective for roofing and below-grade walls.
Foam board panels, made from polystyrene or polyurethane, establish a continuous barrier that diminishes moisture infiltration and boasts mould resistance.
These materials contribute to creating a safer, more comfortable environment for those who prioritise quality, safety, and enduring solutions.
Thermal Performance and R-values
Thermal performance is vital for the effectiveness of waterproof wall insulation, with R-value being a key measure of this performance. R-value indicates how well insulation resists heat flow; higher values signify better resistance. The R-value is influenced by both the type of insulation material and its thickness. Materials with higher R-values typically provide superior insulation performance and can be more cost-effective long-term by reducing energy costs. Common materials like expanded polystyrene demonstrate a decent level of insulation, while polyisocyanurate is noted for its superior effectiveness. The construction of walls and the prevailing climate significantly affect the required R-value, with colder regions necessitating higher ratings to ensure comfort and energy efficiency. Combining different types of insulation and ensuring proper installation can enhance overall thermal performance. Waterproof insulation is particularly important as it helps maintain R-value by preventing moisture accumulation, which can undermine insulation effectiveness and lead to increased heat loss. Choosing the appropriate R-value is essential for achieving better energy efficiency and comfort within buildings.
Moisture and Mold Resistance Characteristics
Moisture absorption differs among insulation materials, with some, such as closed-cell foam and expanded polystyrene (EPS), offering strong resistance to water uptake, thereby aiding in the prevention of mould growth. Properly installed moisture barriers further mitigate the risk by blocking water ingress while allowing vapour to escape. Rigid polyurethane insulation, with its closed-cell structure, prevents water absorption and reduces the likelihood of mould development. Together, these features ensure that walls remain dry and mould-free, even in humid or damp conditions.
Material Moisture Absorption
Materials used for wall insulation differ in their ability to manage moisture and resist mould. Various options, such as spray foam, mineral wool, polyisocyanurate, and cellular glass, exhibit distinct moisture absorption characteristics.
Closed-cell spray foam is highly effective at resisting water, functioning as a moisture barrier that dries rapidly when exposed to wet conditions.
Open-cell spray foam, while not absorbing water like a sponge, may lose its effectiveness if subjected to prolonged moisture.
Mineral wool has a tendency to absorb a considerable amount of water, which can compromise its insulating properties and prolong drying times.
Water contact does not lead to absorption by cured foam. Water typically flows around or through foam if gaps exist. Severe water intrusion can cause foam to break apart. Foam may be displaced by water pressure but remains non-absorbent. Damage can occur due to force, not moisture retention.
Polyisocyanurate absorbs very little moisture and typically dries within a day, thereby maintaining its thermal performance.
Cellular glass is completely waterproof, never absorbing moisture, making it particularly suitable for areas prone to high humidity.
Selecting the appropriate material based on moisture absorption is crucial for constructing a durable, moisture-resistant wall system that enhances the comfort and safety of any home.
Mold Growth Prevention
Effective mould growth prevention relies on more than merely selecting the right insulation materials; it also hinges on proper moisture management strategies.
Installing vapour barriers correctly helps reduce moisture accumulation within walls by blocking the movement of water vapour. These barriers serve as a crucial defence against condensation, keeping insulation surfaces dry and less vulnerable to mould.
The type of vapour retarder backing—foil, paper, or none—affects vapour flow and the associated risks of mould. In moisture-prone areas such as basements and crawl spaces, vapour barriers assist in regulating humidity levels, thereby decreasing the likelihood of mould development.
Combining these barriers with effective ventilation strategies further prevents humid air from stagnating. Proper installation and regular maintenance of vapour barriers are essential to ensure their effectiveness over time.
Utilising moisture meters prior to installation ensures that insulation remains dry, fostering an environment where mould struggles to thrive, ultimately promoting a healthier, more comfortable living space.
Installation and Application Considerations
Proper installation and application of waterproof wall insulation require careful planning and meticulous attention to detail. It starts with thorough surface preparation, such as assessing the existing render to confirm its suitability for new insulation, and safeguarding windows, doors, and pipes from potential damage during the installation process. Additionally, selecting the right type of insulation material that meets building regulations and performance standards is crucial for effectiveness and safety. Installing aluminium starter tracks at the appropriate height provides a level base for insulation panels. The area must be clean, dry, and free from obstructions to ensure effective adhesion. When selecting insulation, factors such as thermal resistance, fire safety, and compatibility with waterproofing systems should be considered. Techniques include fitting the thickest insulation panels first, cutting them accurately, and securing them efficiently with adhesives or fasteners. After installation, sealing all seams, joints, and penetrations with foil tape or sealants is essential to create a reliable vapour and moisture barrier. Proper installation practices are vital to prevent water ingress and ensure the longevity of the waterproofing system. Proper application not only guarantees long-lasting waterproofing performance but also enhances energy efficiency, making it an investment in the longevity and comfort of your building.
Environmental and Safety Factors
Environmental impact and safety are crucial considerations when selecting waterproof wall insulation. Certain materials require significant energy for production and can emit considerable CO2, while others utilise recycled or natural resources that help to minimise environmental harm. Moreover, fire safety measures are imperative, as some insulation types may present fire risks or include chemicals that could compromise indoor air quality. Production energy use significantly influences the overall environmental footprint of insulation materials. Ensuring that insulation materials are both environmentally friendly and safe for use within the home is essential for creating a healthy living environment.
Environmental Impact Considerations
When considering waterproof wall insulation materials, it's essential to evaluate their environmental impacts carefully.
Cellulose insulation is notable for containing a high percentage of recycled content, which significantly helps to reduce its carbon footprint. In contrast, wood fibre insulation, while renewable, often contains petrochemical additives such as paraffin wax or polymer binders, raising concerns about its environmental footprint. Recycled content not only minimizes waste but also reduces the need for virgin resources, contributing to sustainability. Additionally, recycled wood fibres may harbour hazardous substances, including lead-based paint or formaldehyde, which can pose health risks.
Plastic-based insulation options, like expanded polystyrene, are energy-intensive to produce and contribute to CO2 emissions. On the other hand, inorganic insulations, such as fibreglass, generate fewer emissions but still require considerable energy during their manufacturing processes.
Key considerations include:
The benefits of recycled content in minimising waste and reducing resource extraction.
The potential health impacts from chemical additives used in some insulation materials.
The energy consumption associated with manufacturing, which influences the overall environmental impact.
The risk of toxic or non-recyclable materials contributing to landfill waste.
Fire Safety Measures
Fire safety measures for waterproof wall insulation are crucial for minimising the risk of fire and safeguarding building occupants. The NFPA 285 standard plays a significant role in assessing exterior wall assemblies that include combustible foam insulation, evaluating the vertical and lateral spread of flames. While most commercial buildings are required to comply with this standard, residential properties are encouraged to do so, although it is not mandatory. Increasing concerns about fire safety in homes have led to tighter regulations and testing requirements across jurisdictions.
Insulation boards need to adhere to specific evaluations set by manufacturers to ensure safety. Thermal barriers, such as gypsum boards, are implemented to fulfil fire resistance requirements and to slow down the penetration of fire. The proper installation of these barriers is vital for ensuring safety and compliance with building regulations.
The table below outlines key fire safety components:
Component |
Purpose |
Testing Standards |
| NFPA 285 | Prevents flame spread on exterior walls | Full-scale fire testing |
| Thermal Barriers | Shields foam insulation from fire | NFPA 286 & NFPA 275 |
| Flame Retardants | Reduce foam flammability | Product-specific standards |
Adhering to these fire safety measures is essential for the protection of both buildings and their occupants. Incorporating fire detection systems and proper monitoring can further enhance safety and early warning capabilities.
Cost and Longevity Insights
Waterproof wall insulation can vary significantly in both cost and longevity, influenced by the type selected and the specific installation techniques employed.
Exterior wall insulation generally falls within a broad price range, with the overall expense being determined by the size of the property and the materials utilised. Expanding on the costs, labor expenses can constitute a large portion of the total installation fee, especially for extensive or complex projects. Spray foam insulation is on the higher end of the spectrum, offering impressive moisture resistance and durability. Although it may require a greater initial investment, its longevity often justifies the expense.
In contrast, fibreglass insulation presents a more economical option; however, it may not perform as well in damp conditions, potentially leading to a shorter lifespan.
Several factors play a role in determining the final cost of insulation. These include the dimensions of the walls, ease of access for installation, and the selected type of insulation.
Using higher-quality materials tends to yield better results, as they not only last longer but also provide superior resistance to water damage.
Additionally, properties that are larger or more challenging to access can lead to increased overall costs.
Regular inspections and maintenance are crucial to sustaining the effectiveness of your insulation over time, ensuring it continues to perform as intended.
Benefits of Rigid Foam Boards
Rigid foam boards are an exceptionally effective choice for insulating walls, thanks to their outstanding thermal performance. They boast higher R-values per inch compared to traditional materials such as plywood or fibreglass batts, making them efficient in minimising heat loss.
When installed externally, they help reduce thermal bridging, which keeps interiors warmer and contributes to lower energy costs.
Moreover, rigid foam serves as a moisture barrier, safeguarding wood and framing from water ingress and mould development, particularly beneficial in damp climates.
These boards also enhance air sealing, effectively diminishing draughts and increasing overall comfort. Their durability and impressive compressive strength ensure reliable long-term performance, resisting pests and water damage.
Additionally, rigid foam boards are straightforward to install, making them a practical solution for improving waterproofing and insulation in any building.
Metal Wool and Its Unique Properties
Metal wool, often known as mineral wool, is a versatile insulating material crafted from natural rocks such as basalt and industrial byproducts like slag.
It primarily consists of blast furnace slag combined with natural rock. The raw materials are melted and spun into fibres, resulting in mats or batts ideal for insulation purposes. During production, recycled scrap and waste materials are typically incorporated, thereby minimising environmental impact.
Due to its inorganic composition, metal wool is resistant to mould and doesn't contain organic binders that could foster microbial growth.
This unique material offers several significant advantages:
Low thermal conductivity, making it an effective insulator
Moisture resistance that mitigates dampness and mould
Naturally non-combustible, able to endure high temperatures
Exceptional sound absorption and structural stability
These characteristics render metal wool a dependable choice for building insulation, ensuring safety, efficiency, and enduring performance.
Choosing the Right Insulation for Your Walls
When selecting insulation for walls, understanding the various types available can assist homeowners in making informed choices that align with their needs and budgets.
Spray foam insulation offers exceptional air sealing and moisture resistance, with options for both open-cell and closed-cell varieties. However, it necessitates professional installation, which can add to the overall cost.
Rigid foam board insulation delivers consistent thermal performance, with types like extruded polystyrene (XPS) and polyisocyanurate (polyiso) providing strong moisture resistance. This makes them suitable for both external and internal applications.
Fibreglass insulation is a cost-effective option, easy to install, and resistant to mould. However, it can allow air infiltration if not properly sealed, which may affect its overall effectiveness.
Cellulose insulation is an eco-friendly choice that performs well but is susceptible to moisture, which should be considered in damp areas.
When selecting insulation, take into account factors such as cost, moisture resistance, and ease of installation to ensure the best fit for your project.
Here’s a summary of the key benefits of each insulation type:
Insulation Type |
Key Benefits |
| Spray Foam | Air sealing, moisture resistance |
| Rigid Foam Board | Consistent thermal performance, moisture resistant |
| Fibreglass | Cost-effective, simple DIY installation |
| Cellulose | Eco-friendly, effective insulation |
Ultimately, it is vital to match insulation to your specific requirements and budget to achieve optimal results.
Conclusion
Choosing the appropriate waterproof wall insulation is influenced by various factors such as climate, budget, and individual requirements. Rigid foam boards and mineral wool provide excellent moisture resistance, each presenting distinct advantages.
Correct installation, alongside consideration of safety and environmental impacts, is vital for ensuring long-lasting protection. By familiarising themselves with the characteristics of different materials, homeowners can make well-informed decisions that enhance wall durability, prevent mould growth, and deliver dependable insulation for years to come.
Understanding the differences in insulation types, such as thermal performance and moisture control, will aid in selecting the best option for your specific situation. Select materials that not only meet your insulation needs but also align with sustainability goals, ensuring a more eco-friendly approach to home improvement.
In summary, making educated choices about waterproof wall insulation can greatly improve the comfort and longevity of your living space.