- Blogs
- Full Fill vs Partial Fill Cavity Wall Insulation Board
Full Fill vs Partial Fill Cavity Wall Insulation Board

Cavity wall insulation is a very important element in building construction, contributing to improved energy efficiency and decreased heat loss. If your home was built after the 1930s, it likely features cavity walls – an external construction comprising two 'skins' of masonry (brick or blockwork) with a gap, or cavity, between them. This cavity, initially designed primarily to prevent dampness from penetrating the inner wall, also presents a significant opportunity for thermal improvement. Uninsulated walls can be responsible for as much as a third of a home's total heat loss. Two primary types of cavity wall insulation exist: full fill and partial fill. Understanding the differences is key to making an informed choice for your property.
Full-fill insulation entails completely filling the cavity with insulation material, forming an unbroken thermal barrier that improves energy efficiency, minimizes heat transfer pathways, and reduces air infiltration. By eliminating air movement within the cavity and maximising the volume of insulation, full fill aims to achieve the highest possible thermal resistance. However, meticulous installation is necessary to prevent thermal bridging (where heat bypasses the insulation through more conductive elements), and this method can be more costly than partial fill insulation.
Conversely, partial fill insulation leaves an empty space, known as a residual cavity, between the insulation and the outer masonry leaf. While it is often considered easier and faster to install in new build scenarios, potentially more cost-effective in some cases, and designed with moisture management in mind, it may result in air gaps if not perfectly installed, and could have lower overall insulation effectiveness compared to a perfectly executed full-fill insulation system. It is primarily suited for new constructions rather than retrofitting existing buildings, as installing boards into a sealed cavity is generally impractical.
These distinctions in installation process, effectiveness, cost, and suitability for new construction or retrofitting differentiate full fill and partial fill cavity wall insulation. The choice also significantly impacts compliance with UK Building Regulations, particularly concerning thermal performance (Part L), fire safety (Part B), and moisture resistance (Part C).
TLDR; Too Long, Didnt Read
- Full fill insulation completely fills the wall cavity, aiming for maximum thermal performance. It's the standard choice for retrofitting existing homes with materials like blown-in mineral wool or beads.
- Partial fill insulation uses rigid boards and intentionally leaves an air gap (a residual cavity). This design provides robust protection against moisture and is primarily used in new-build construction.
- For moisture-prone areas (e.g., severe wind-driven rain), partial fill is often the safest choice, though some full-fill systems are certified for these conditions.
- Full fill generally offers better soundproofing, while partial fill with high-performance PIR boards can achieve excellent thermal U-values in a thinner profile.
- The choice depends on whether the project is a new build or retrofit, the property's location, and compliance with UK Building Regulations (Part L for thermal, Part B for fire, Part C for moisture).
Full Fill Cavity Insulation 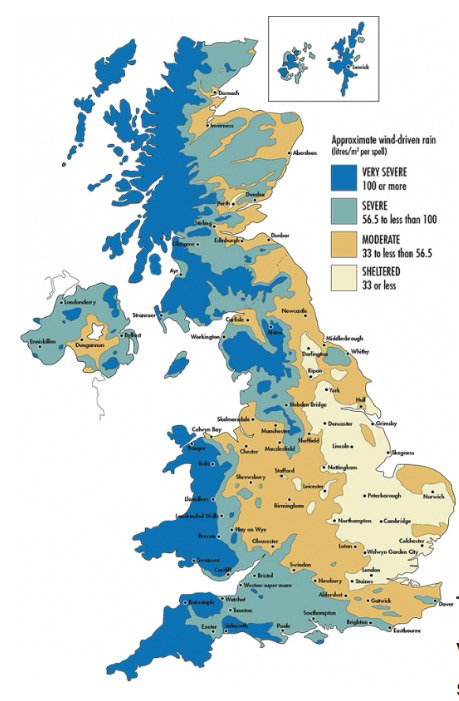
Full fill cavity insulation completely fills the cavity and creates a continuous thermal barrier, maximizing energy efficiency and improving overall insulation effectiveness. This method aims to achieve the highest possible thermal resistance by eliminating air movement within the cavity. When installing full fill cavity insulation, it is important to follow specific installation techniques to ensure optimal performance. This includes using suitable insulation materials that are designed to fill the cavity dimensions and provide a high level of thermal resistance.
Common materials for full fill include blown mineral wool (rock or glass wool fibres), bonded expanded polystyrene (EPS) beads, injected polyurethane (PUR) foam, and cellulose fibre. Each of these is typically installed by specialist contractors using dedicated equipment to blow or inject the material into the cavity through a series of drilled holes in the external masonry for retrofit applications, or by installing mineral wool batts in new constructions. By completely filling the cavity, full fill insulation eliminates potential pathways for heat transfer and reduces air infiltration, resulting in improved energy efficiency and potentially contributing positively to a property's Standard Assessment Procedure (SAP) rating and Energy Performance Certificate (EPC).
One of the key advantages of full fill cavity insulation is its ability to prevent thermal bridging. Thermal bridging occurs when there is a direct conduction path between the interior and exterior of a building, bypassing the insulating layer, often through structural elements. With full fill insulation, the continuous thermal barrier minimizes the risk of thermal bridging, ensuring that heat is not lost or gained through these components. Some full fill materials, like injected polyurethane foam, can also improve the structural stability of the wall by bonding the inner and outer leaves together.
Full Fill Cavity Wall Construction is Not Recommended in All Areas
It is important to note that a fully filled cavity is not recommended in some parts of the country, particularly those in severe or very severe wind-driven rain exposure zones as defined by UK Building Regulations (Part C) and BRE guidance, due to the risk of moisture penetration. Therefore, the design and construction of the cavity wall must comply with the relevant sections of the product’s Agrément Certificate (e.g., from the BBA - British Board of Agrément), which will specify its suitability for different exposure conditions and any particular construction requirements. A thorough pre-installation survey by a qualified professional is essential to assess site-specific conditions and the suitability of the existing wall construction.
If using full-fill insulation batts (such as mineral wool batts), this specialist cavity wall product is designed to perform at its best when the gaps between boards are kept to a minimum. This is achieved by using precision straight edges. The quality and accuracy of the brickwork and blockwork are also important, as they must ensure that there is consistent contact and complete filling of the intended cavity space.
For batt installation, the boards should never be pushed into a pre-built cavity after both leaves are up. Instead, the inner leaf should always be constructed ahead of the outer leaf. This will allow any mortar to be cleaned off the back of the inner leaf before the boards are installed.
Building control surveyors and warranty providers like LABC Warranty will also inspect the work as it progresses to ensure that mortar snots, spacer placement (if applicable to the system), and inaccurate bricklaying do not compromise the installation. This will help to ensure that the wall performs as it is designed to. For blown or injected full-fill systems, the drilling pattern for injection holes must adhere to the BBA certificate for the specific system to ensure even distribution and a complete fill without voids.
Can PIR be used as full fill cavity insulation?
Generally, standard PIR (Polyisocyanurate) insulation boards are designed for partial fill applications, not full fill.
However, there are specific, specially engineered PIR products that are designed and BBA-certified for full fill cavity applications.
Here's the breakdown:
-
Standard PIR Boards: These are typically used in partial fill systems where a clear 50mm residual cavity is maintained. The primary reason is for moisture management; this gap allows any rainwater that penetrates the outer brickwork to drain away harmlessly. If you used a standard PIR board to completely fill the cavity, it could risk trapping moisture.
-
Specialised Full Fill PIR Boards: Manufacturers like Celotex, Recticel, and Unilin have developed specific PIR boards for full fill use such as Celotex Thermaclass Cavity Wall 21.
-
How They Work: These boards have engineered features, such as tongue-and-groove edges, that lock together tightly. This design creates a continuous, water-resistant barrier across the joints, preventing moisture from tracking across the insulation to the inner wall.
-
BBA Certification: These products undergo rigorous testing to prove they can be used in a full fill capacity without compromising the wall's resistance to moisture. They will have a specific BBA (British Board of Agrément) certificate that explicitly states they are fit for use in defined full fill cavity wall applications.
-
Summary of Full Fill
With care and skill, a high-performance solution can be achieved that will keep the householder warm and cosy, while also reducing energy costs.
When compared to other insulation methods, full fill cavity insulation offers superior energy efficiency benefits when correctly installed. The complete filling of the cavity eliminates air gaps and reduces the overall heat loss, resulting in reduced energy consumption and lower heating and cooling costs. Additionally, the continuous thermal barrier provided by full-fill insulation improves the insulation effectiveness, maintaining a more consistent and comfortable indoor temperature. Full fill systems can also offer better soundproofing compared to partial fill.
However, it is important to note that full fill cavity insulation, especially injected or blown systems, requires professional expertise and specialised equipment for installation, as precise techniques are necessary to ensure proper filling and avoid thermal bridging or settlement (for loose-fill materials if not installed to the correct density). While the availability of suitable insulation materials for full fill cavity insulation is generally good, the choice may be influenced by factors like cavity width (very narrow cavities, often less than 50mm, may be unsuitable) and exposure zone. Blown or injected full fill insulation is a very common and practical method for retrofitting existing empty cavity walls. Full fill batts are typically used in new construction projects.
The initial cost can sometimes be higher than partial fill, due to the volume of material or specialised installation, with indicative costs for blown systems ranging from £475 to £800 for an average property, potentially rising to £1,500 or more for larger detached houses.
Partial Fill Cavity Wall Insulation 
Partial fill cavity wall insulation, typically using rigid insulation boards (such as Polyisocyanurate (PIR) or Phenolic foam boards), offers a robust option for moisture management and is primarily suited for new build projects where boards can be installed as the masonry work progresses. It provides an easier and quicker installation process in this context compared to building in full fill batts. This type of insulation is available in a range of materials, making it accessible for homeowners and builders focusing on new constructions.
However, it is important to note that partial fill insulation may leave air gaps between the insulation boards or between the boards and the inner leaf if not meticulously installed. This can potentially lead to reduced insulation effectiveness and thermal bridging. The maintained residual air cavity is important for preventing moisture transfer from the outer leaf to the inner leaf, making it suitable for all UK exposure zones, including those with very severe wind-driven rain.
In terms of cost comparison, partial fill cavity wall insulation generally tends to be more affordable in material volume if thinner high-performance boards are used to achieve a target U-value, but labour costs for careful installation must be considered. Retrofitting partial fill boards into existing sealed cavities is generally impractical and not a common approach.
When it comes to energy efficiency comparison, partial fill insulation offers a significant improvement over uninsulated walls. It helps reduce heat loss and energy consumption, leading to lower heating and cooling costs. However, full fill insulation, when perfectly installed, provides a more continuous thermal barrier, potentially offering higher overall energy efficiency compared to partial fill insulation.
Overall, partial fill cavity wall insulation is a reliable solution for new buildings, particularly where moisture management is a key concern. While it may have drawbacks such as the critical need for precise installation to avoid gaps and ensure the integrity of the residual cavity, it still provides significant energy efficiency benefits. Proper installation to ensure boards are tightly butted, correctly fixed, and the residual cavity is kept clear of mortar droppings is important to ensure its performance and effectiveness in reducing heat loss and improving energy efficiency.
Benefits of Full Fill Cavity Insulation
One advantage of cavity insulation that completely fills the space is its ability to create a continuous thermal barrier. This means that there are no gaps or air pockets within the insulation (when installed correctly), which maximizes its energy efficiency and improves its overall insulation effectiveness. By completely filling the cavity, full fill cavity insulation eliminates potential pathways for heat transfer and reduces air infiltration, resulting in reduced heat loss and energy consumption. It can also offer superior acoustic insulation compared to partial fill systems.
In terms of installation process, full fill cavity insulation requires precise installation to avoid thermal bridging and ensure a complete fill. Thermal bridging occurs when there is a direct pathway for heat transfer through materials with high thermal conductivity, such as metal framing or masonry ties. Therefore, proper installation techniques and attention to detail are important to ensure that the insulation is properly installed and thermal bridging is minimized. For blown or injected systems, this means adhering to the correct drilling patterns and ensuring consistent material flow and density. For batt systems, it means ensuring tight fitting and no gaps.
However, retrofitting full fill cavity insulation in existing buildings using batt-based systems can be challenging and is generally not done; blown or injected full fill materials are the standard for retrofit. These methods require professional expertise and specialised equipment. The availability of suitable insulation materials for full fill cavity insulation is generally good, covering various performance needs and budgets.
Drawbacks of Partial Fill Cavity Wall Insulation
A drawback of partial fill insulation is the potential for air gaps between the insulation and masonry, or between adjacent boards, which can compromise its overall effectiveness in reducing heat loss and energy consumption. These potential air gaps can occur due to improper installation or poorly cut/fitted boards. When air gaps exist, heat can easily transfer through these gaps by convection, leading to thermal bridging concerns or thermal bypass. Thermal bridging occurs when there is a direct pathway for heat transfer between the inside and outside of a building, bypassing the insulation's thermal resistance. As a result, the insulation's effectiveness in preventing heat loss is lower compared to perfectly installed full fill insulation, where the entire cavity is filled without any gaps.
Another limitation of partial fill insulation is its generally lower soundproofing capabilities compared to full fill systems, as the residual air cavity does not contribute significantly to sound dampening.
Partial fill cavity wall insulation also requires meticulous site practice during construction to ensure the residual cavity remains clear of mortar droppings and debris, which could bridge the cavity and negate its moisture management benefits. While the insulation boards themselves are durable, the overall system's performance relies heavily on the quality of installation and detailing.
What is a residual cavity?
The residual or nominal cavity in a partial fill cavity wall insulation system serves two primary purposes. First and foremost, its main function is to provide a clear, unbridged space that acts as a barrier to moisture, allowing any rainwater that penetrates the outer masonry leaf to drain harmlessly down the cavity face of the outer leaf and out through weep holes. This significantly reduces the risk of dampness reaching the inner wall. Secondly, it allows the bricklayer to more easily position the outer leaf of brick or block during construction. This would be more difficult and time-consuming if the cavity were fully filled with rigid insulation boards right up to the outer leaf during the build process.
When using foil-faced insulation boards (like PIR or some phenolic boards), the low-emissivity aluminium facing of the insulation board reflects radiant heat back across the air space, which can improve the thermal performance of the cavity, provided the cavity is sealed and the foil remains clean. Insulation retaining discs on wall ties are used to maintain the specified clear cavity between the insulation facing and the outer leaf; a 10mm air space is sometimes cited as optimum for the thermal benefit of low-emissivity facings, but the overall residual cavity width is primarily dictated by moisture management and construction tolerances.
The minimum residual cavity width is often cited as 25mm for buildings up to 12m high in less exposed locations. This is the minimum width considered to prevent moisture from penetrating the inner leaf of the wall. However, it is widely recommended by industry bodies and Building Regulations guidance to design for a 50mm clear residual cavity to allow for normal inaccuracies in the building process and ensure effective drainage. This means that the cavity boards can be installed without any gaps on their warm side, while maintaining a robust clear space on their cold side, which will help to prevent moisture from penetrating the wall.
In areas of very severe exposure to wind-driven rain, such as coastal areas or regions identified by BRE exposure maps (as per Approved Document C of the Building Regulations), a 75mm residual cavity may be required. This is because the wind and rain in these areas can be more likely to cause moisture to penetrate the outer leaf of the wall.
It is absolutely important to keep the residual cavity clean and free of mortar snots and debris that can bridge the gap and help moisture cross the cavity to the inner leaf or the insulation itself. This can be done by careful bricklaying, cleaning mortar droppings from board edges and wall ties as work progresses, and potentially using cavity battens or boards during construction to catch falling mortar.
Above doors, windows and other openings, a cavity tray must be installed to intercept water running down the cavity and direct it outwards through weep holes, thereby protecting the lintel and the inside of the building. A cavity tray is a damp-proof course (DPC) built into the wall. The cavity tray should have weepholes (at least two per opening, spaced at a maximum of 900mm centres, and always at stop-ends) to allow the collected moisture to drain away. Cavity trays must also be installed with stop-ends to prevent water from running off the ends of the tray and back into the cavity or onto the inner leaf.
Cavity trays may also be needed for projections and discontinuities within the cavity such as ring beams, or at roof abutments. A ring beam is a concrete beam that is used to support the lintel above a door or window opening, or at floor levels. The ring beam can create a discontinuity in the cavity, which can allow moisture to penetrate the wall if not properly detailed with a cavity tray.
The specific requirements for residual cavity width and detailing will vary depending on the location of the building, its height, the exposure rating, the type of masonry finish, and the specific insulation system being used. It is important to consult with local building control authorities and refer to the BBA certificate for the chosen insulation product to confirm the requirements for a particular project.
Choosing the Right Cavity Wall Insulation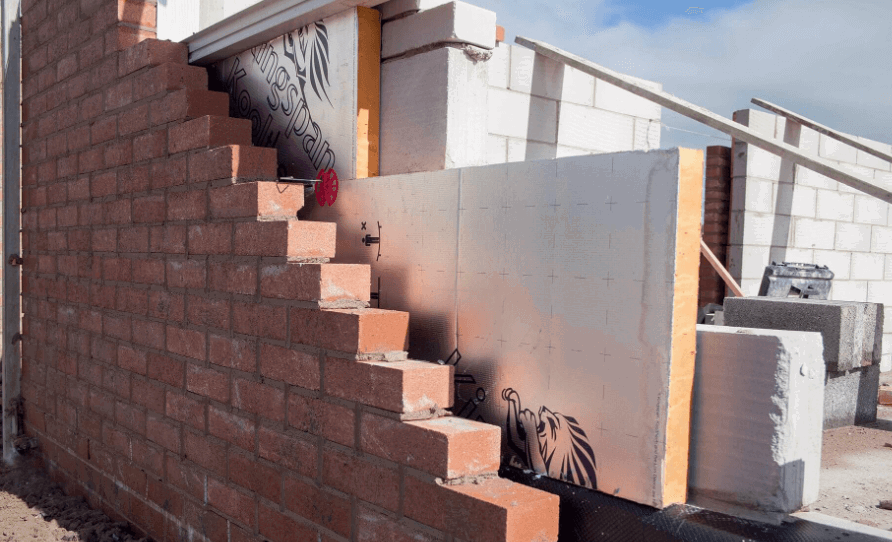 
When selecting the appropriate insulation method for a building, it is important to consider factors such as thermal performance targets (U-values as required by Part L of the Building Regulations), cost-effectiveness, ease of installation (especially differentiating new build from retrofit), and retrofitting suitability. The age and construction type of the property, existing cavity width and condition, local exposure to wind-driven rain, fire safety requirements (Part B of the Building Regulations), the overall moisture management strategy for the building, and environmental impact (GWP, recycled content) of the materials are all vital considerations.
Cost considerations play a significant role in determining the most suitable insulation method for cavity walls. Full fill cavity insulation may be more expensive than partial fill insulation in some scenarios due to the higher material volume or specialised installation costs. However, the potentially superior thermal performance of a perfectly installed full fill system can result in significant energy savings in the long run.
Thermal bridging is another important consideration when choosing the right cavity wall insulation. Full fill insulation, by its nature, aims to minimize thermal bridging by creating a continuous thermal barrier. Partial fill insulation, if boards are not fitted correctly with tight joints and no gaps behind them, may have areas where heat transfer can occur more readily, impacting the overall insulation effectiveness and energy efficiency of the building. Careful detailing at junctions (wall/floor, wall/roof) and around openings using appropriate cavity closers is essential for both systems to minimise thermal bridging.
Retrofitting challenges should also be taken into account. Full fill insulation using blown or injected materials is generally the most suitable and common method for retrofitting existing empty cavity walls. Full fill batts and partial fill boards are primarily for new construction, as it is generally impractical to retrofit these into existing sealed cavities without significant disruption. On the other hand, partial fill insulation is a robust option for new builds, particularly in high moisture exposure zones. Regular maintenance of the building's exterior (e.g., pointing, render, rainwater goods) is important to protect any cavity wall insulation system.
Finally, the choice of insulation material options is a key factor in selecting the right cavity wall insulation.
For full fill applications, common materials include:
- Mineral Wool (Rockwool or Glass Wool): Available as blown fibres for retrofit or batts for new build. Offers good thermal and acoustic performance and is non-combustible (typically Euroclass A1). Requires careful installation to achieve correct density and avoid slumping (for blown fibre) or gaps (for batts).
- Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) Beads: Small, lightweight beads, usually bonded with an adhesive during injection. Offers good thermal performance and excellent moisture resistance as the beads allow water to drain. Typically Euroclass E or F fire rating.
- Polyurethane (PUR) Foam (Injected): Expands to fill the cavity, offering excellent thermal performance and air tightness, and can add structural stability. Highly moisture resistant. Installation is important and must be done by specialists. Fire performance varies (can be Euroclass E or better if treated).
- Cellulose Fibre: Made from recycled newspaper treated with fire retardants. Offers good thermal and acoustic performance and is hygroscopic (can buffer moisture). Typically Euroclass B or C. Requires specialist installation.
For partial fill applications (primarily new build, using rigid boards):
- Polyisocyanurate (PIR) Boards: Offer excellent thermal performance (low lambda values, typically around 0.022 W/mK) allowing for thinner insulation layers. Usually foil-faced. Fire performance is often Euroclass E or F, which restricts use in taller buildings.
- Phenolic Foam Boards: Offer superior thermal performance (lambda values around 0.018−0.019 W/mK), allowing for the thinnest insulation solutions. Also typically foil-faced. Fire performance is often Euroclass F, also limiting high-rise applications.
- Mineral Wool Batts/Slabs: Can also be used for partial fill, offering excellent fire resistance (Euroclass A1) and good thermal/acoustic properties, though may require greater thickness than foam boards for the same U-value.
It is important to consider the specific requirements of the building, such as soundproofing capabilities, fire regulations for the building type and height, and moisture exposure, in order to make an informed decision. Always consult BBA certificates for specific product performance and installation guidelines.
Insulation and Installation of Wall Insulation Boards
The process of insulating, whether through full or partial fill, mandates exactitude and professional input.
During partial fill installations in new builds, insulation boards (such as PIR or phenolic foam boards, or mineral wool batts) are methodically positioned and fixed against the inner leaf of the cavity wall as it is constructed, establishing a uniform and efficient insulation layer while maintaining a clear residual cavity (typically 50mm) to the outer leaf. Key aspects include ensuring boards are tightly butted, securely fixed with appropriate wall ties and retaining clips, and that the cavity remains free of mortar droppings.
Full fill blown wall insulation (using materials like mineral wool fibres, EPS beads, or cellulose) for retrofitting existing cavities constitutes another technique that demands meticulous execution by specialist installers. This involves drilling a series of small holes in the external wall's mortar joints, through which the insulation material is blown into the cavity using specialised equipment to ensure a complete fill without voids and at the correct density to prevent settlement.
Wall insulation boards, made from diverse materials including PIR, and mineral wool, present adaptability in electing the right insulation for specific project needs. The choice between full and partial fill methods hinges on a detailed assessment of cavity composition, property type (new build or existing), exposure conditions, and the sought-after thermal performance, contributing to a masonry wall with energy efficiency and insulation prowess.
Contrasting Full Fill and Partial Fill Approaches
Choosing between full-fill and partial-fill cavity insulation depends upon numerous considerations, encompassing cavity width, exposure to wind-driven rain, building type (new or existing), and the desired insulation value (U-value).
Partial fill insulation options, typically rigid boards like PIR or phenolic foam, or mineral wool batts, are primarily used in new builds. They show versatility and, when installed correctly, ensure a clear residual air space to robustly manage moisture penetration, making them suitable for all UK exposure zones. Preventing thermal bridging with partial fill relies on meticulous fitting of the boards against the inner leaf and ensuring continuous insulation around openings and junctions.
Conversely, full-fill solutions aim to completely saturate the cavity. For retrofitting existing properties, blown mineral wool, EPS beads, or injected polyurethane foam are common. In new builds, full-fill mineral wool batts or products like Celotex Thermaclass Cavity Wall 21 (a PIR board BBA-certified for full-fill applications) can be used. These systems aim for maximum thermal resistance by eliminating the air cavity. However, their suitability in high moisture exposure zones needs careful assessment based on the specific material and BBA certification.
Opting for the Right Cavity Insulation Type
When choosing the ideal insulation for masonry cavity walls, a detailed grasp of the building's needs, its location, and regulatory requirements takes precedence. Perusing product datasheets, BBA certificates (like that for Thermaclass Cavity Wall 21), and manufacturer's literature yields invaluable insights into its specifications and applications. Variables such as insulation value (target U-value to meet Part L of Building Regulations), installation simplicity (and whether it's new build or retrofit), fire performance (Euroclass rating and Part B compliance), moisture resistance, and synergy with other components in the wall's constitution inform the judicious selection of insulation type. This decision carries significant weight in terms of energy efficiency, long-term building health, and adherence to building regulations. Whether realized through complete cavity saturation or partial fill techniques, precise installation by competent, and preferably accredited (e.g., CIGA registered for retrofit), installers ensures a thermally efficient masonry cavity wall, fostering a sustainable and comfortable constructed milieu. A pre-installation survey by a qualified professional is always recommended.
Our Cavity Wall Products Range
- Knauf Dritherm 37 - Mineral Wool Cavity Wall Insulation: A water-repellent glass mineral wool slab for full-fill masonry cavity walls. It typically has a thermal conductivity (lambda) of 0.037 W/mK and achieves a Euroclass A1 reaction to fire classification (non-combustible). It is BBA certified for use in all exposure zones when installed according to the certificate.
- Celotex Thermaclass Cavity Wall 21 - Cavity Wall Insulation Board: A PIR insulation board with a very low thermal conductivity of 0.021 W/mK. It is BBA certified for full fill cavity wall applications and can be installed with a minimal 10mm residual cavity or as a complete full fill. It uses a blowing agent with low Global Warming Potential (GWP) and zero Ozone Depletion Potential (ODP). This product should not be used in the external walls of buildings over 11 metres in height due to fire regulations.
- Knauf Dritherm 32 - Cavity Batt Insulation: A high-performance glass mineral wool slab, often with a lower lambda value (around 0.032 W/mK) than Dritherm 37, offering improved thermal performance. It is also typically Euroclass A1 (non-combustible) and BBA certified for full-fill applications.
- Isover Cavity Wall Slab (CWS) 32: A glass mineral wool slab providing thermal performance (lambda 0.032 W/mK) in external masonry cavity walls. It is manufactured with a water repellent binder and is BBA approved for both full and partial fill applications. It achieves a Euroclass A1 reaction to fire.
- Isover Cavity Wall Slab (CWS) 36: Similar to CWS 32, this glass mineral wool slab offers good thermal performance (lambda 0.036 W/mK) and is also BBA approved for full and partial fill applications with a Euroclass A1 fire rating. It is made with up to 82% recycled glass.
- Celotex CW4000 - PIR Cavity Wall Insulation: This is a polyisocyanurate (PIR) insulation board specifically designed for partial fill cavity wall applications. It has a thermal conductivity of 0.022 W/mK and features a low emissivity foil facing. It is BBA approved for partial fill use but has a Euroclass F reaction to fire and should not be used in external walls of buildings over 11 metres in height.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for general guidance and informational purposes only. It is not intended to constitute professional or technical advice, and you should not rely on it as such. All building work, including the specification and installation of insulation materials, must comply with current UK Building Regulations and relevant standards. Before undertaking any work or making any decisions regarding cavity wall insulation, you should

Samuel Hitch
Managing Director
Buy Insulation Online.
Leave A Reply
Your feedback is greatly appreciated, please comment on our content below. Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *