Acoustic Plasterboard
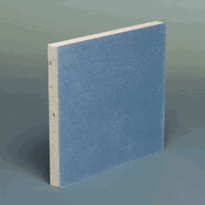
Acoustic plasterboard features a denser gypsum core combined with specialized additives, including paper liners with tapered edges and a distinctive blue hue, to enhance soundproofing. Its increased density improves sound reduction, impact resistance, and surface hardness, making it suitable for various environments that require noise control.
Installation involves a robust framework, layered panels often combined with acoustic insulation such as mineral wool, and meticulous sealing of joints to prevent sound leaks.
Further details highlight how careful selection, configuration, and precise fixing optimize acoustic performance, enabling informed application in noise-sensitive spaces.
Composition and Structure of Acoustic Plasterboard
Acoustic plasterboard is specially designed to enhance sound insulation within interior constructions, primarily through its distinct composition and structural features. Its core material is gypsum, which provides a non-combustible element essential for safety. To improve soundproofing, the core is manufactured to be denser than standard plasterboard, often incorporating specialized additives that increase density, surface hardness, and impact resistance. The manufacturing process is adapted to achieve this higher density, resulting in superior sound-dampening qualities. The dense gypsum core is sandwiched between paper liners on both faces and along the edges, with tapered edges to facilitate seamless jointing. The front-facing paper typically features a blue hue, serving as a visual identifier. These design elements combine to produce a robust, effective component for isolating sound in various interior spaces. Additionally, the manufacturing process involves specific techniques to uniformly increase the core density, which plays a crucial role in enhancing its soundproofing capabilities.
Enhancing Soundproofing Performance With Acoustic Plasterboard
Improving soundproofing performance with acoustic plasterboard involves assessing multiple factors that influence the overall effectiveness of sound insulation in interior constructions. The sound reduction performance is typically expressed through a weighted sound reduction index, or Rw, which depends on the components of the building assembly, such as stud type and spacing, cavity insulation like acoustic mineral wool (AMW), and the number of plasterboard layers installed. Soundproof plasterboard is engineered specifically with these factors in mind to optimize results. Incorporating AMW enhances sound absorption within the cavity, while applying two layers of plasterboard on each side of the partition considerably increases soundproofing ratings compared to a single layer. The design of the assembly—including stud spacing and plasterboard thickness—is essential in achieving optimal results.
Feel confident knowing your efforts are creating quieter, more peaceful spaces where you belong.
Experience the satisfaction of lowering noise levels, fostering harmony and focus within your environment.
Trust that your investments enhance comfort, safety, and property value, strengthening your sense of community.
Practical Applications and Installation Considerations
Practical applications of acoustic plasterboard are diverse, encompassing a range of settings where sound transmission control is vital. These include residential dwellings, commercial offices, institutional facilities such as schools and hospitals, and specialized spaces such as home cinemas and recording studios.
Effective installation begins with constructing a robust framework using either steel or timber studs. Layers of plasterboard are fixed horizontally to this framework, ensuring consistent placement. Joints between boards should be carefully sealed with resilient sealant to prevent sound leaks. To enhance acoustic performance, an acoustic membrane, such as QuietWave®, can be positioned between plasterboard layers, forming a sound-absorbing barrier.
Fixing methods are crucial for maintaining soundproof integrity. Panels can be glued directly to walls or fixed into the stud framework with screws, depending on the nature of the surface and the desired level of sound insulation. It's essential to ensure secure attachment without compromising acoustic properties. Proper measurement and leveling during installation are vital, as is the strategic placement of screws to avoid weak points.
Minimizing service openings and ensuring that all edges are properly sealed further enhances the system’s ability to prevent sound leakage. When attaching electrical or plumbing services, care should be taken to make cuts precise and reseal junctions with appropriate acoustic sealants.
Post-installation finishing involves plastering over joints, taping seams, and performing regular inspections to confirm the integrity of the acoustic barriers. Well-maintained acoustic plasterboard systems can provide long-lasting noise control, significantly improving the quality of indoor environments.
Conclusion
Acoustic plasterboard offers an effective solution for enhancing sound insulation within a variety of building environments through its specialized composition and structure. For optimal soundproofing performance, correct installation techniques—such as precise placement and sealing—are essential. This material is well-suited for a range of applications, including shared walls and recording studios, providing a dependable means of controlling noise transfer. Paying careful attention to installation practices ensures superior results, making acoustic plasterboard a valuable component in sound management strategies for both residential and commercial buildings in the UK.