- Blogs
- How to Insulate Walls: Techniques and Products
How to Insulate Walls: Techniques and Products

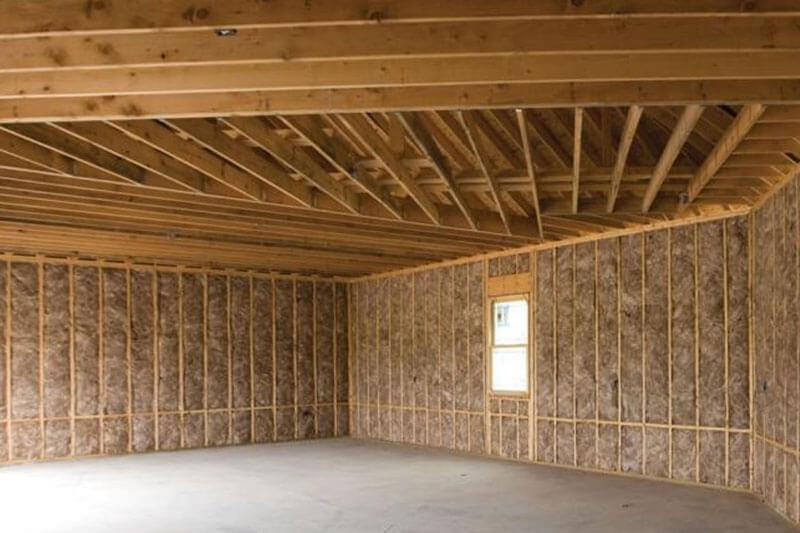
Wall insulation is a material put inside walls to minimise heat loss, noise transmission, and improve overall energy efficiency. Correctly insulated walls may significantly improve your house's comfort while lowering energy expenditures.
Insulating walls is a key phase in the total house insulation process, and it may be accomplished using a range of materials and techniques. In this complete guide, we'll look at several types of wall insulation, things to consider before you insulate your walls and advice for successful wall insulation.
Insulation Methods:
There are two major solid wall insulation methods
External Wall Insulation
External wall insulation involves fixing insulation boards to the exterior of the building. This method is suitable for buildings that are difficult to insulate from the inside, or for those that require a facelift.
External wall insulation can help to improve the appearance of a building, as well as increase its thermal performance. Insulation will also save internal floor space. This method is effective in reducing noise and condensation as well.
Internal Wall Insulation![internal wall insulation]()
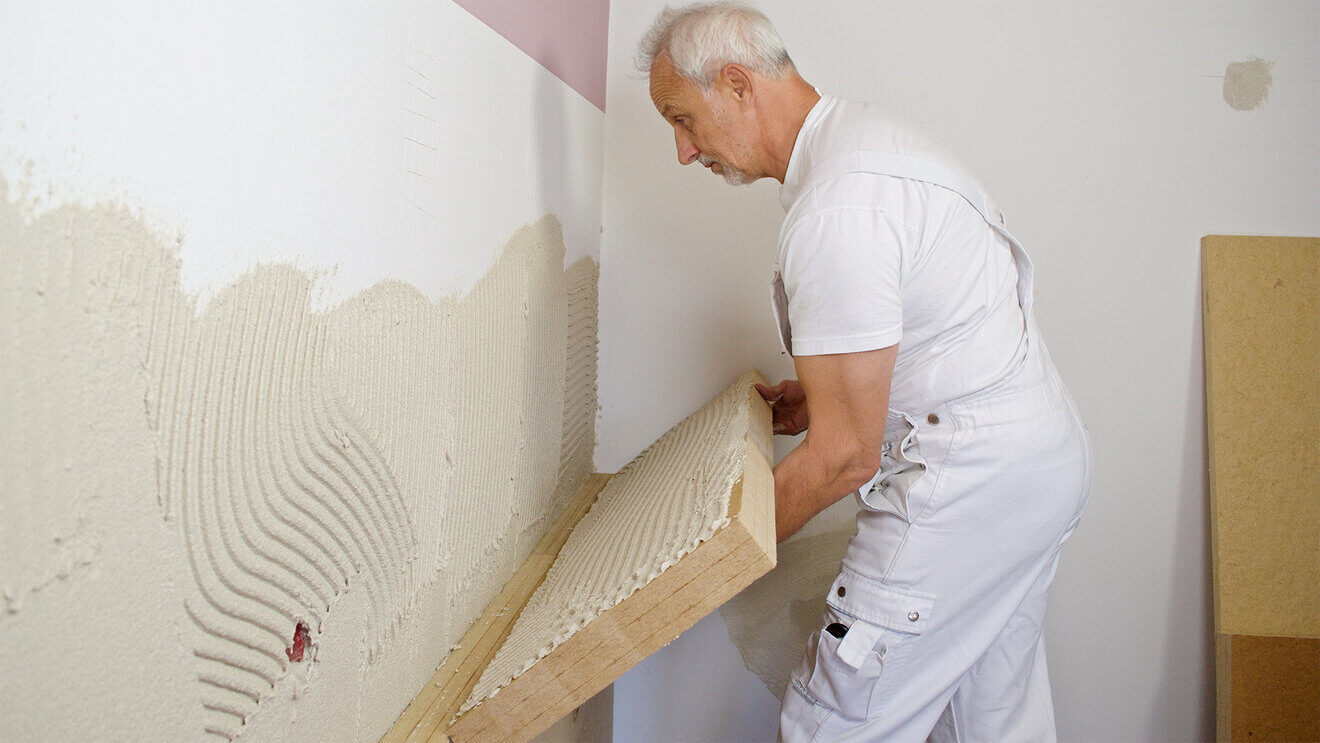
Internal wall insulation involves adding insulation boards or mineral wool slabs to the interior of the building. This method is suitable for buildings that cannot be insulated from the outside, or for those that require minimal disruption.
Internal insulation can help to improve the thermal performance of a building, as well as reduce noise and condensation. However, it can reduce the living space, as the insulation takes up some floor space.
Wall Insulation Products
Let's look at some of the best and most popular wall insulation products.
1. PIR Insulation
PIR insulation (polyisocyanurate) is foam insulation used to insulate walls. PIR insulation is a valuable material for reducing heat loss and increasing energy efficiency due to its high thermal resistance (R-value).
PIR insulation is made of a rigid foam that contains isocyanurate resin and polyol. It is frequently wrapped on one or both sides with foil or plastic laminate to produce a vapour barrier and boost thermal resistance. Because it is lightweight, easy to install, and has high compressive strength, PIR insulation is a popular choice for commercial and residential building projects.
2. Insulation Slabs![Insulation slabs]()
Insulation slabs, or batt insulation, are insulation materials commonly used to insulate building walls, ceilings, and floors. Insulation slabs are pre-cut sizes that fit between the conventional spacing of wall studs, joists, and rafters and are constructed of materials such as fibreglass insulation and Rockwool insulation. These days, eco-insulating materials like Sheepwool, wood fibre or hemp wool, which offer better insulation, last longer and allow for a healthier living space.
Insulation slabs are available with or without a face material, such as kraft paper, foil, or non-woven fabric, which adds moisture management, fire protection, and ease of installation. The R-value of an insulating slab is determined by its thickness, which evaluates the material's resistance to heat flow. A higher R-value denotes improved insulation performance.
3. Insulation Boards
Insulation Boards are flat panels constructed of insulating materials that have good thermal efficiency. Foam plastics, phenolic and wood fibre are some of the materials that may be used to make these boards. Insulation boards are commonly used to limit heat transmission between the interior and outside of a structure in walls, floors, and roofs. They can also be utilised to increase fire resistance and limit noise transmission.
4. Insulated Plasterboards
Insulated plasterboard, made by combining insulation boards like PIR, EPS or XPS and plasterboard, can be a good way to insulate walls. They are easy to install and offer good thermal insulation.
Insulated plasterboards additionally save space as they combine the insulation and drylining into one easy-to-use product. They can be added to existing walls internally. They can be fixed to walls using the dot-and-dab method or other using mechanical fixtures and fittings, much like other insulation boards
Buy Insulated Plasterboards Now
5. Polystyrene Insulation Boards
Polystyrene Insulation Boards are insulation boards constructed of polystyrene foam. Polystyrene insulating boards are classified into expanded polystyrene (EPS) and extruded polystyrene (XPS).
EPS polystyrene insulation boards are created by expanding and moulding tiny beads of polystyrene foam into big boards. Because of their low R-value (thermal resistance), these boards are frequently utilised for low-cost insulation applications such as insulating concrete blocks or beneath concrete slabs.
Polystyrene foam is extruded and compressed into boards to create XPS polystyrene insulation boards. Since they offer a greater R-value than EPS boards and are more moisture-resistant, these boards are a popular choice for use in external insulation and finishing systems (EIFS)
What are the different types of Wall Insulation?
Depending on the type of wall you have, you can either opt for:
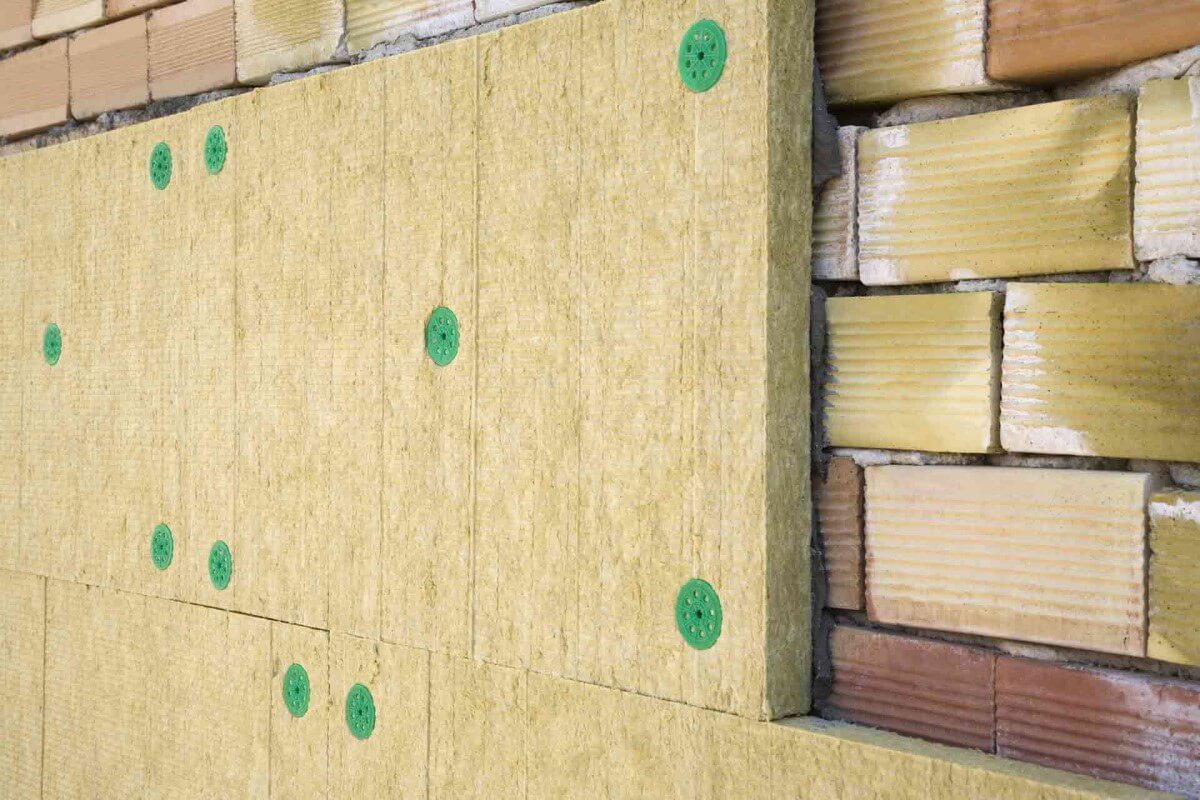
1. Stud Wall Insulation![batt insulation]()
Stud Wall Insulation is the process of providing insulation to the voids between the wooden studs that make up the frame of a wall in a structure. This is often done on interior walls, and it is an efficient approach to increasing a building's energy efficiency and comfort.
Insulation materials for stud walls include fibreglass or mineral wool batts, cellulose spray foam insulation, wood fibre, sheep wool and hemp insulation. Stud walls can then be covered with plasterboards or insulated plasterboards. Your choice of insulation would, however, depend on the environment, required insulation and budget.
2. Cavity Wall Insulation
Cavity walls are made up of two layers of brick or block, separated by a gap (cavity). Cavity wall insulation involves filling this gap with insulating material, such as fibreglass, mineral wool, foam, or beads. A building or home has cavity if it was built after the 1920s. Cavity wall insulation can help to reduce heat loss by up to 35%.
Cavity walls are insulated using fibreglass batts or PIR cavity boards. Some of the best cavity wall insulation we stock include, Celotex Thermaclass 21, Knauf Dritherm and Celotex PIR cavity Boards
Buy Cavity Wall Insulation Now
3. Solid Wall Insulation
Solid walls are typically found in older buildings that do not have a cavity. Solid walls can be insulated either externally or internally.
In the case of external solid wall insulation, the insulation is fixed to the exterior of the wall, which is then covered with a render or cladding. Internal solid wall insulation involves adding insulation boards to the inner side or inside the wall, followed by plasterboard. Solid wall insulation can help to reduce heat loss by up to 45%.
What to consider before insulating?
Various aspects should be considered when insulating walls to achieve optimum insulation performance and efficiency. These elements include:
-
Climate: The kind and amount of insulation required depends on the environment in which a structure is located. Buildings in colder areas, for example, may require stronger insulation or materials with better insulating properties, to decrease heat loss and enhance energy efficiency. Buildings in hotter regions may require greater R-value insulation to decrease cooling expenses.
-
Type of Wall: The kind of wall construction also influences the choice of insulation material. Various forms of insulation are required for different types of walls, such as wood frames, masonry, or concrete. Moreover, the thickness and spacing of studs or joists within walls may influence insulation selection.
-
Cost: Insulation costs vary based on the material utilised, thickness, and R-value. Investing may be advantageous if higher-quality insulation with a higher R-value can result in considerable energy savings over time. Examining the initial cost of the insulating material and installation and the possible long-term energy cost reductions is critical.
-
Safety: While choosing insulation, safety is also an important element to consider. While handling insulation, it is critical to wear suitable safety equipment and follow manufacturer guidelines for safe installation. If not handled appropriately, several forms of insulation, such as fibreglass, can irritate the skin, eyes, and respiratory system.
Tips for Effective Wall Insulation![steico]()
Proper wall insulation may considerably enhance a building's energy efficiency and comfort. Various suggestions and strategies may be employed when insulating walls to achieve the highest efficiency and maximum energy savings. They include:
-
Seal air leaks: Air leaks in walls can impair the efficacy of insulation greatly by enabling warm or cold air to escape and outside air to permeate. Air leaks can be sealed using weather stripping or caulking to increase insulation performance and save energy expenses.
-
Cover electrical outlets: Electrical outlets in walls can cause minor air leaks, reducing the efficacy of insulation. Foam gaskets installed under outlet covers can assist in sealing these gaps and increase insulation performance.
-
Install a vapour barrier: A vapour barrier is a substance that helps to keep moisture out of walls, where it can cause damage or mould development. A vapour barrier between the insulation material and the inner wall can increase insulation performance while protecting the wall from moisture damage.
How to insulate walls in simple steps
1. Determine the type and amount of insulation needed for your walls. This will depend on the climate, the age and type of the building, and the insulation rating required by local building regulations.
2. Remove any existing insulation that may be in the walls, if necessary. This may involve cutting open the drywall, so be prepared for some mess and dust.
3. Cut insulation batts or blankets to the right size and shape to fit between the wall studs. Alternatively, spray insulation can also be used to fill cavities and cover the surface of the wall.
4. Install the insulation by gently pressing it into place between the studs, ensuring that there are no gaps or spaces where air can escape. Use a staple gun to hold the insulation in place if needed.
5. Replace any drywall or other wall coverings that were removed during the insulation process. Seal around any electrical boxes or other wall fixtures to prevent drafts.
6. Optional: add a vapour barrier over the insulation to prevent moisture buildup. This may not be necessary for all climates and situations.
7. Inspect your walls periodically to ensure that the insulation is still in good condition and has not shifted, settled, or been damaged by pests or water.
Conclusion:
Ultimately, wall insulation is a critical component of a well-insulated structure. By adequately insulating walls, building owners and occupants can benefit from enhanced comfort, decreased energy costs, and less environmental impact. To obtain the optimum insulation effectiveness and efficiency, consider aspects such as climate, wall type, cost, and safety before insulating walls.
If you're looking for some top-quality, energy-saving insulation for your cavity wall, external or internal walls, look no further than Buy Insulation Online. We are the UK's leading insulation suppliers of insulated plasterboards, batts, rigid insulation boards, eco insulation like wood fibre, sheep's wool, hemp wool and more. If you are ever confused about the right insulating option for you our experts are just a call away!

Samuel Hitch
Managing Director
Buy Insulation Online.
Leave A Reply
Your feedback is greatly appreciated, please comment on our content below. Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *