- Blogs
- The History of Insulation
The History of Insulation

Insulation has been around for decades, but only recently did it become popular in modern homes. Due to the rising energy bills and energy shortage, insulation has become a necessity nowadays.
The roots of insulation can be traced back to the Ancient Egyptians and Vikings, who used the cooling properties of mud to build their homes and put straw and mud between logs to insulate them. The Greeks also used insulation, including asbestos, for its flame resistance.
Let's retrace the history of some common insulation materials that we have used over the years.
Asbestos
The use of asbestos for insulation dates back to the late 1800s. Asbestos fibres are resistant to heat, water, electricity, and chemical damage. Hence, they were an ideal insulator for boilers and steam engines.
Because of its thermal insulation properties, asbestos became popular among builders and manufacturers. Its high tensile strength and fire resistance made it an ideal choice for insulation. It was often mixed with cement for better insulating properties.
It was not until the early 20th century that research began to show that asbestos exposure was hazardous for workers. Back in the time, there were no government regulations in place for asbestos hence, many deaths and health issues were reported.
In 1930, Dr Montague Murray documented the first death from asbestos exposure. This discovery spurred other countries to take action. This led the countries to switch to mineral wool and other forms of insulation.
In the 1970s, the Environmental Protection Agency began to restrict the use of asbestos. Today, many consumers prefer to use products without asbestos.
Cellulose Insulation
Cellulose is a naturally occurring substance, in use as an insulating material for centuries. Its use dates back to cavemen, and in fact, Thomas Jefferson himself used cellulose in the construction of his mansion, Monticello, in 1769. 
However, it wasn’t until the early twentieth century that the concept of using cellulose in buildings became popular. The use of cellulose as an insulator was accelerated after WWII and continued to grow throughout the 1970s and 1980s.
In the past, cellulose was criticised for settling into walls, but dramatic improvements in the manufacturing process have helped to eliminate that problem. In the early 20th century, cellulose insulation was a low-tech product. It was primarily produced as sound-deadening material for buildings but soon became a popular insulating material.
Although the early versions of cellulose insulation lacked modern fibre technology and application equipment, the materials still provided efficient thermal insulation for buildings.
The energy crisis in the 1970s prompted a boom in interest in cellulose insulation, and it became one of the most common types of insulation used in modern buildings. While some companies were unable to keep up with the demand, most continued to improve their materials and processes to meet growing customer demand.
Today, cellulose insulation is used as loose-fill insulation. It is used to insulate the loft, as cavity wall insulation and so on.
A major drawback of cellulose insulation is its ability to absorb water. The moisture can make the insulation sag and create void spaces, which reduces its insulation value.
In addition, the chemicals used to protect cellulose from water can be corrosive. Research also indicates that metal fasteners, plumbing pipes, and electrical wires can become corroded when exposed to wet cellulose.
Fibreglass Insulation
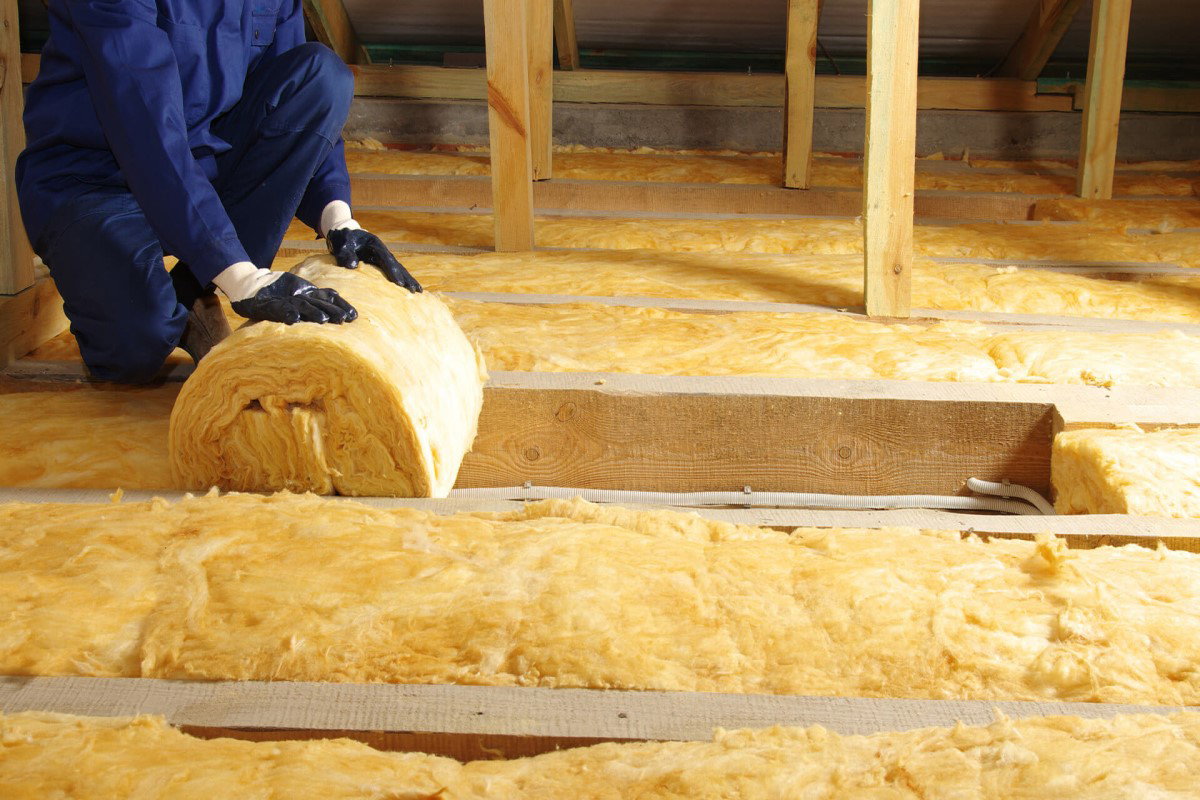 Fibreglass insulation is a popular choice for insulating homes. It has been the go-to choice for insulation across projects for many years.
Fibreglass insulation is a popular choice for insulating homes. It has been the go-to choice for insulation across projects for many years.
Fibreglass insulation is used in many forms, including pre-cut batts and rolls, blown-in loose-fill insulation and more. Fibreglass insulation slabs and rolls are used to insulate walls, lofts, roofs and much more.
They can also be used to insulate pipes. Fibreglass pipe insulation protects pipes from freezing and soundproofs them.
Fibreglass insulation is cheaper than most other insulating materials. It is environmentally friendly since it is made from recycled glass containers and silica sand.
Glass wool insulation was first made in the 1930s when researchers attempted to make weatherproof walls from transparent glass. The breakthrough came when molten glass was hit by compressed air. This produced tiny fibres, which were patented in 1936. Eventually, fibreglass was used in the construction industry and became the industry standard.
While fibreglass insulation is used in many common products, it is associated with health risks.
Tiny particles in fibreglass insulation can lodge in the skin and enter the lungs. They can cause rashes and itchiness.
Additionally, tiny glass particles in the fibres of glass wool insulation can irritate the eyes and nose. They can also cause respiratory problems and even cancer.
When installing fibreglass insulation ensure you wear at least a mask and gloves. Fibreglass insulation must be dealt with only by appropriate PPE kits.
Rock Wool Insulation
In addition to fibreglass, mineral wool insulation or stone wool insulation is also a widely popular insulating material. It is used to insulate pipes, walls, floors and much more.
Though the process of making rock wool was patented as early as the 1870s, it was only commercially viable in the 1950s.
Mineral wool insulation is made using stone and slag, hence the name stone wool or rock wool. It has a slightly better thermal conductivity when compared to fibreglass insulation.
Rock wool insulation is also better at soundproofing compared to fibreglass. Though it is a bit costlier compared to fibreglass, it is yet to show any negative impacts on health or surroundings.
Cavity wall insulation
The history of cavity walling can be traced back to the 19th century when architects and builders began using hollow walls in buildings. They were first introduced in northern Europe and became more popular in the 1920s. These hollow or cavity walls were used for various reasons, including enhanced stability, fire resistance, and protection against the weather.
Modern cavity wall construction uses metal or plastic ties to avoid the capillary transfer of moisture. Early cavity-walled buildings were particularly breathable, allowing for good moisture exchange between the interior and outdoor environments. This is a very important aspect when considering cavity wall insulation and repair. 
To insulate cavity walls you can use fibreglass cavity batts like Dritherm 32 and 37 or Superwall 36 and 32, Cavity walls can also be insulated using PIR boards like Celotex CW4000. Other options include cellulose insulation, EPS boards and foam insulation.
Spray Foam Insulation
There are many uses for spray foam insulation. They are used to insulate lofts, walls and much more. However, it can pose some risks if improperly installed.
Although the number of residential and commercial projects utilising this material is steadily rising, bad installations can result in odours, moisture problems, and fire safety issues. For this reason, it’s crucial to hire trained installers and follow proper application guidelines.
The history of spray foam insulation began in the 1940s when industrial chemist Otto Bayer began working with polyurethane foam. In the early 1940s, the Bayer and Monsanto corporations partnered to produce Mobay, a wartime product that was used in military and aviation applications.
Today, spray foam insulation is an important staple of modern insulation. Although it became popular in the 1980s, it was used for years before that. Today, spray foam insulation is a cost-effective and energy-efficient alternative to traditional insulation, such as fibreglass.
Foil Insulation:
Foil insulation, multifoils, and reflective barrier are some different names for foil insulation. It is basically a reflective foil backing on one or both sides of one or more substrates.
Foil insulation is not new, though it only gained popularity recently, thanks to the space insulator. The use of foil as insulation dates back to 1892 when Sir James Dewer first tested its insulating properties and used it for the "Dewer Flask", also known as a Thermos or vacuum flask.
Foil insulation is probably the simplest and most effective way to keep heat out. Foil insulation works differently compared to traditional insulation. It stops the transfer of heat through all three modes -conduction, convection and radiation, something that fibreglass or wool insulation fails to do.
Today, Foil insulation can be used to insulate walls, roofs and even pipes. Foil-faced insulation is quite commonly used to insulate ducts, pipes, walls and other applications. Foil insulation rolls help you hit the required U-values and save energy and space.
In Conclusion:
Insulation has evolved and so have our requirements. While the basic need is to keep ourselves warm from the freezing temperatures outside, that alone is no longer sufficient.
Researchers continue to explore new and innovative ways to improve the energy efficiency of a building and find more techniques, materials and tools to keep the heat in, so changes in insulation materials and insulating techniques are something that we need to look forward to.
For trade-quality insulation, insulation slabs, boards, foil insulation rolls, duct insulation, pipe lagging, valve jackets and more, visit Buy Insulation Online. With every order, we plant a tree for free and also save five trees in the Amazon.

Samuel Hitch
Managing Director
Buy Insulation Online.
Leave A Reply
Your feedback is greatly appreciated, please comment on our content below. Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *