- Blogs
- Thermal Insulation Materials - A Brief Guide
Thermal Insulation Materials - A Brief Guide

Ever since the UK announced its goal to be carbon neutral by the 2050s, a lot of schemes, rules and regulations have been announced to put things in motion.
This coupled with the ever-increasing energy prices, and power shortage has forced people to look for sustainable and innovative ways to maintain comfortable indoors without burning a hole in their pockets. Insulation saves energy and keeps your home warm, cosy and comfortable all year long.
As building regulations have evolved, insulation materials have developed considerably. There have been improvements in the insulation performance of traditional mineral wool insulation, plus we can see new relatively inventions like foil insulation rolls etc, ruling the market today.
All these changes are driven by the common aim to meet the standard needs under the Building Regulations Component L and to comply with government carbon decrease targets. In this article, we will be discussing some basic concepts of insulation.
Basics Modes of Heat Transfer
Insulation items are created to stop or at least minimize the transfer of heat throughout the application. Insulation in its many forms like - insulation boards, insulation on a roll, or insulation batts, work to prevent heat transfer by one or all three mechanisms below.
Convection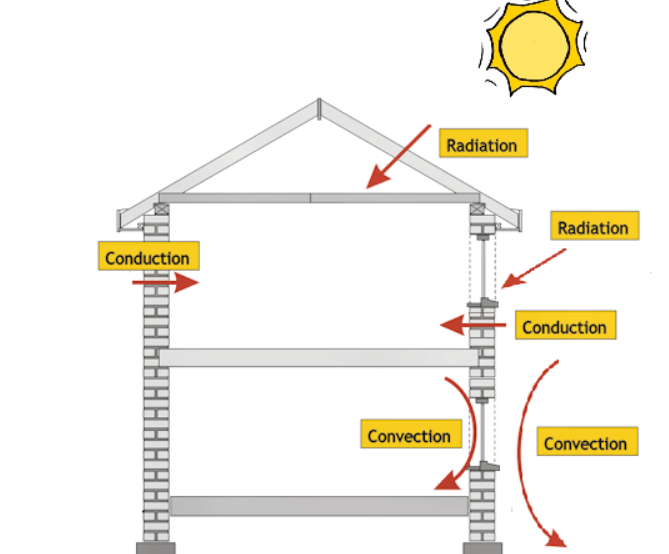
Convection mainly takes place in liquids or gases. An ideal example of convection would be boiling water. As the water heats up it moves upwards and away from the source of heat. In homes or buildings, the cracks or tiny gaps in doors and windows can let chilly air in, and the warm air can move out due to convection.
Radiation
Radiant heat can only travel in straight lines and it is the only mode of heat transfer in a vacuum. Radiation is when heat radiates across the space between you and surrounding objects in your home.
Conduction
Conduction is how a majority of heat transfer takes place. Contact between two materials of different temperature levels leads to an exchange of heat until both attain equilibrium.
How Does Insulation Work?
Insulation materials are made of items that are bad conductors of heat. Mineral wool insulation, fibreglass insulation rolls, foam insulation boards like PIR, and polystyrene insulation all restrict the transfer of heat through at least one or two modes of heat transfer.
However, not many insulation materials can stop heat transfer through radiation. Foil Insulation rolls or multifoils are your best bet to restrict heat loss through radiation. They reflect heat to the source, thus keeping your homes cool in the summer.
Foil-faced insulation like PIR boards, ductwrap, Kingspan kooltherm or Isover pipe lagging also reflects radiant heat thanks to their external foil-facings.
How To Choose The Right Insulation Material?
Insulation materials must be chosen based on their performance, finish, core-make and ofcourse, your application. The specification of materials that insulate is basically a science-based choice.
However, it is important that the person who chooses these insulation materials has the required knowledge and can understand not only the mathematical performance but also the outer elements that can influence the final set-up.
Insulation requirements are frequently based upon the need to meet the minimum Building Regulations Component L, to hit the target U-Values and efficiency of the insulating material itself.
In order to define the insulation requirements of a building correctly, the insulation contractor must understand the reasons why the said insulation materials work, as well as use the correct modern technology for any given building information.
How To Measure Thermal Insulation Efficiency?
The thermal insulation efficiency of any insulating material is measured in terms of R-value, U-Value and K-values.
Thermal Conductivity (K or Lamda values)
Insulation materials restrict the circulation of heat between two bodies that are at different temperatures. Greater insulation efficiency is directly attributed to the thermal conductivity of the insulant or the material. A lower thermal conductivity or K-Value means the insulating material is poor at conducting heat, that is, it better resists the transfer of heat through its fabric.
This means heat loss through the structure is restricted, meaning heat stays in and lowers energy bills. Thermal conductivity is a constant for any type of product and is gauged in W/mK (watts per kelvin meter)
R-Value
The straight inverse of their conductivity is the thermal resistance of a material or R-Value. It gauges the product's ability to resist the transfer of heat.
Thermal resistance is described as the 'R-value of a material. The R-value is computed from the thickness of the product split by its thermal conductivity. It is gauged in terms of m2K/W (square metre kelvins per watt). A greater R-value indicates that the material is better at restricting heat transfer.
U-value
In building and construction terms, U-value can be credited to a single density of any material, however, it is much more accurate to calculate it as a product of the assembly of various products in any type of given type of building and construction.
The U-value accounts for the transmission of heat through a pre-determined area of the structured fabric i.e, the amount of heat lost or gained in one sq.m of a given area. It is expressed in W/m2K (watts per square metre kelvin)
Types Of Insulation Materials
Insulation materials can be broadly classified into two different types based on their cell nature:
Open Cell Insulation:
Open cell insulation consists of wool insulation products such as mineral and sheep wool insulation etc.
Any open-cell insulation material has many millions of tiny open-cell air pockets that are produced during its manufacture.
The production proc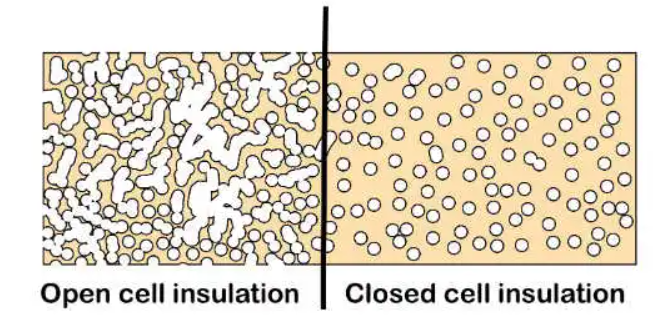 ess forces air into the core of the wool fibres, and a formerly introduced binding agent is activated to form a matrix locking the make-up with each other. This technique allows these wool insulation products to restore their shape as well as density even after compression.
ess forces air into the core of the wool fibres, and a formerly introduced binding agent is activated to form a matrix locking the make-up with each other. This technique allows these wool insulation products to restore their shape as well as density even after compression.
Basically, the open cell nature of the fabric allows free air movement, but the path is not easy and quite tortuous therefore, heat loss is restricted. The air pockets can also trap the heat, minimising their loss.
Open-cell insulation is also breathable in nature. They allow water vapours to pass through their fabric. This majorly helps with preventing condensation and other moisture-related issues.
Closed Cell Insulation:
Closed cell insulation includes insulation boards like PIR boards, polystyrene insulation and others. The manufacturing process of closed cell insulation involves the controlled introduction of gases (blowing agents) that helps develops a far more dense matrix of specific cells than mineral wool insulation. The cells are formed as bubbles of the gas whose thermal conductivity is significantly less than that of air.
The cell walls are incredibly thin which restricts transmission, yet are gas-tight.
Closed cell insulation is not breathable and does not promote a free movement of air within its fabric. The thick cell structure restricts the capacity for gas movement, allowing it to relocate only within the boundaries of the cell itself.
Based on the material makeup and type, Insulation can be divided into the following types:
Blanket insulation:
Insulation batts, slabs and insulation rolls together are known as blanket insulation. They are generally made of wool insulation be it fibreglass, mineral wool, sheep wool, and so on.
Batt insulation made of mineral wool can be used for stud-wall insulation, internal wall insulation, floor insulation, pitched roof insulation, cavity wall insulation and so on.
Insulation rolls can be used to insulate walls, lofts, and so on. Specialized insulation rolls like ductwrap can be used to insulate ductwork.
Blanket insulation has low thermal conductivity. Mineral wool, in general, gives superior sound and fire insulation. They are breathable and open-cell in nature.
Foam Insulation Boards:
Foam insulation boards like PIR, polystyrene insulation or boards made of hemp wool, wood fibre insulation and so on are closed-cell in nature. With thermal conductivity as low as 0.022 W/mK they ensure superior thermal insulation in every application.
Insulation boards are used to insulate walls, roofs, floors (EPS and XPS boards) and so on.
Foil Insulation:
The unique property of foil insulation to reflect and prevent heat loss by radiation is what sets it apart from traditional wool insulation. With foil insulation rolls and panels, you can easily achieve the required U-values for wall and roof insulation.
At Buy Insulation online, we stock foil insulation rolls like YBS SuperQuilt, Superfoil SF19+, Actis Hybris and so on. They can be used to insulate walls, and pitched roofs.
Insulated Plasterboards:
Insulated Plasterboards combine the goodness of drylining and insulation in one product. They can be of different types based on the type of insulating material.
For eg: Knauf XPS laminate plus is a combination of extruded polystyrene and plasterboards, while Celotex PL4000 or Xthratherm thermal liner combines PIR insulation and drylining.
Insulated plasterboards can be used to insulate roofs, external walls, internal walls and so on. They save space and are more effective compared to wool insulation.
How to Install Insulation?
To make your home more energy efficient, you will have to insulate walls, lofts, roofs, and floors. Pipe insulation cannot be neglected and neither can the ducts in the crawl spaces. However, it is critical that you insulate these properly.
Employ certified contractors for the job. Research, discuss and decide on the right insulation materials for your application. If you want to take up installing loft insulation or pipe insulation as a DIY project, make sure you follow the manufacturer's guidelines property and also refer to videos and other information on the manufacturer's website. Also, ensure that you meet the required building regulations in the process.
It is important that you do pre-installation checks, especially before insulating loft, cavity walls etc. Cavity batts like Dritherm 32, and Dritherm 37 can only work to their optimal performance if they are installed properly and there are no pre-existing moisture problems in cavities.
Insulation materials made with modern technology last for quite a long time. However, this can only happen if the condition is ideal, which it rarely is. So, ensure you hire certified professionals for the job and conduct periodic checks on the insulation.
Conclusion:
Insulation materials rely upon their inherent molecular makeup, to minimize heat transfer through the three modes discussed above. While insulating a building is probably the only way to effectively restrict heat loss, it needs to be done right to reap the maximum benefits.
For trade-quality loft roll, acoustic insulation, ductwrap, pipe lagging, valve covers, and more visit Buy Insulation Online. On every order, we plant a tree for free and also save five trees in the Amazon!

Samuel Hitch
Managing Director
Buy Insulation Online.
Leave A Reply
Your feedback is greatly appreciated, please comment on our content below. Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *